Dynamic landscape and evolution of m6A methylation in human
- PMID: 32406913
- PMCID: PMC7293016
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaa347
Dynamic landscape and evolution of m6A methylation in human
Abstract
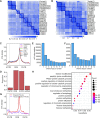
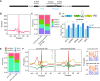
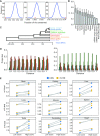
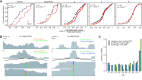
m6A is a prevalent internal modification in mRNAs and has been linked to the diverse effects on mRNA fate. To explore the landscape and evolution of human m6A, we generated 27 m6A methylomes across major adult tissues. These data reveal dynamic m6A methylation across tissue types, uncover both broadly or tissue-specifically methylated sites, and identify an unexpected enrichment of m6A methylation at non-canonical cleavage sites. A comparison of fetal and adult m6A methylomes reveals that m6A preferentially occupies CDS regions in fetal tissues. Moreover, the m6A sub-motifs vary between fetal and adult tissues or across tissue types. From the evolutionary perspective, we uncover that the selection pressure on m6A sites varies and depends on their genic locations. Unexpectedly, we found that ∼40% of the 3'UTR m6A sites are under negative selection, which is higher than the evolutionary constraint on miRNA binding sites, and much higher than that on A-to-I RNA modification. Moreover, the recently gained m6A sites in human populations are clearly under positive selection and associated with traits or diseases. Our work provides a resource of human m6A profile for future studies of m6A functions, and suggests a role of m6A modification in human evolutionary adaptation and disease susceptibility.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evolutionary Implications of the RNA N6-Methyladenosine Methylome in Plants.Mol Biol Evol. 2022 Jan 7;39(1):msab299. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msab299. Mol Biol Evol. 2022. PMID: 34633447 Free PMC article.
-
N6-Methyladenosine Methylomic Landscape of Lung Tissues in Murine Acute Allergic Asthma.Front Immunol. 2021 Oct 19;12:740571. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.740571. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34737744 Free PMC article.
-
A novel RT-QPCR-based assay for the relative quantification of residue specific m6A RNA methylation.Sci Rep. 2019 Mar 12;9(1):4220. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-40018-6. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30862814 Free PMC article.
-
Role of m6A RNA methylation in cardiovascular disease (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2020 Dec;46(6):1958-1972. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2020.4746. Epub 2020 Oct 6. Int J Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 33125109 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functions of N6-methyladenosine and its role in cancer.Mol Cancer. 2019 Dec 4;18(1):176. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1109-9. Mol Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31801551 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
m6A-TSHub: Unveiling the Context-specific m6A Methylation and m6A-affecting Mutations in 23 Human Tissues.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2023 Aug;21(4):678-694. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2022.09.001. Epub 2022 Sep 9. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2023. PMID: 36096444 Free PMC article.
-
m6A RNA methylation in brain injury and neurodegenerative disease.Front Neurol. 2022 Sep 8;13:995747. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.995747. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36158961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Silencing of METTL3 prevents the proliferation, migration, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and renal fibrosis of high glucose-induced HK2 cells by mediating WISP1 in m6A-dependent manner.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Jan 29;16(2):1237-1248. doi: 10.18632/aging.205401. Epub 2024 Jan 29. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38289593 Free PMC article.
-
FTO negatively regulates the cytotoxic activity of natural killer cells.EMBO Rep. 2023 Apr 5;24(4):e55681. doi: 10.15252/embr.202255681. Epub 2023 Feb 6. EMBO Rep. 2023. PMID: 36744362 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-omics analysis of m6A modification-related patterns based on m6A regulators and tumor microenvironment infiltration in lung adenocarcinoma.Sci Rep. 2021 Oct 22;11(1):20921. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-00272-z. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34686691 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li S., Mason C.E.. The pivotal regulatory landscape of RNA modifications. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 2014; 15:127–150. - PubMed
-
- Dominissini D., Moshitch-Moshkovitz S., Schwartz S., Salmon-Divon M., Ungar L., Osenberg S., Cesarkas K., Jacob-Hirsch J., Amariglio N., Kupiec M. et al. .. Topology of the human and mouse m6A RNA methylomes revealed by m6A-seq. Nature. 2012; 485:201–206. - PubMed
-
- Li X., Xiong X., Yi C.. Epitranscriptome sequencing technologies: decoding RNA modifications. Nat. Methods. 2016; 14:23–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

