Are pangolins the intermediate host of the 2019 novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2)?
- PMID: 32407364
- PMCID: PMC7224457
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008421
Are pangolins the intermediate host of the 2019 novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2)?
Erratum in
-
Correction: Are pangolins the intermediate host of the 2019 novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2)?PLoS Pathog. 2021 Jun 9;17(6):e1009664. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009664. eCollection 2021 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2021. PMID: 34106988 Free PMC article.
Abstract
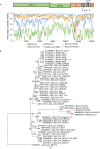
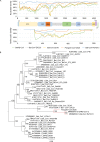
The outbreak of a novel corona Virus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in the city of Wuhan, China has resulted in more than 1.7 million laboratory confirmed cases all over the world. Recent studies showed that SARS-CoV-2 was likely originated from bats, but its intermediate hosts are still largely unknown. In this study, we assembled the complete genome of a coronavirus identified in 3 sick Malayan pangolins. The molecular and phylogenetic analyses showed that this pangolin coronavirus (pangolin-CoV-2020) is genetically related to the SARS-CoV-2 as well as a group of bat coronaviruses but do not support the SARS-CoV-2 emerged directly from the pangolin-CoV-2020. Our study suggests that pangolins are natural hosts of Betacoronaviruses. Large surveillance of coronaviruses in pangolins could improve our understanding of the spectrum of coronaviruses in pangolins. In addition to conservation of wildlife, minimizing the exposures of humans to wildlife will be important to reduce the spillover risks of coronaviruses from wild animals to humans.
Conflict of interest statement
No authors have competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

