Comparative analysis of plastid genomes within the Campanulaceae and phylogenetic implications
- PMID: 32407424
- PMCID: PMC7224561
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0233167
Comparative analysis of plastid genomes within the Campanulaceae and phylogenetic implications
Abstract
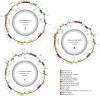
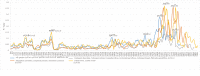
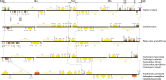
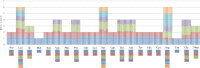
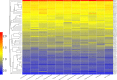
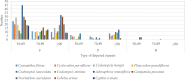
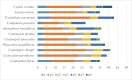
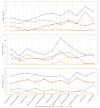
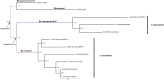
The conflicts exist between the phylogeny of Campanulaceae based on nuclear ITS sequence and plastid markers, particularly in the subdivision of Cyanantheae (Campanulaceae). Besides, various and complicated plastid genome structures can be found in species of the Campanulaceae. However, limited availability of genomic information largely hinders the studies of molecular evolution and phylogeny of Campanulaceae. We reported the complete plastid genomes of three Cyanantheae species, compared them to eight published Campanulaceae plastomes, and shed light on a deeper understanding of the applicability of plastomes. We found that there were obvious differences among gene order, GC content, gene compositions and IR junctions of LSC/IRa. Almost all protein-coding genes and amino acid sequences showed obvious codon preferences. We identified 14 genes with highly positively selected sites and branch-site model displayed 96 sites under potentially positive selection on the three lineages of phylogenetic tree. Phylogenetic analyses showed that Cyananthus was more closely related to Codonopsis compared with Cyclocodon and also clearly illustrated the relationship among the Cyanantheae species. We also found six coding regions having high nucleotide divergence value. Hotpot regions were considered to be useful molecular markers for resolving phylogenetic relationships and species authentication of Campanulaceae.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Lammers TG. World checklist and bibliography of Campanulaceae. Richmond: Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew; 2007b. pp. 1–675.
-
- Schönland S. Campanulaceae In: Engler A, Prantl K, editors. Die Naturlichen Pflanzenfamilien. Leipzig, IV; 1889. pp. 40–70.
-
- Cellinese N, Smith SA, Edwards EJ, Kim ST, Haberle RC, Avramakis M, et al. Historical biogeography of the endemic Campanulaceae of Crete. J Biogeogr. 2009; 36(7): 1253–1269.
-
- Hong DY, Wang Q. A new taxonomic system of the Campanulaceae s.s.: system of Campanulaceae s.s. J Syst Evol. 2014; 53(3): 203–209.
-
- Lee KJ, You HJ, Park SJ, Kim YS, Jeong HG. Hepatoprotective effects of Platycodon grandiflorum on acetaminophen-induced liver damage in mice. Cancer Lett. 2002; 174(1): 73–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

