Bronchial Rheoplasty for Treatment of Chronic Bronchitis. Twelve-Month Results from a Multicenter Clinical Trial
- PMID: 32407638
- PMCID: PMC7462406
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.201908-1546OC
Bronchial Rheoplasty for Treatment of Chronic Bronchitis. Twelve-Month Results from a Multicenter Clinical Trial
Abstract
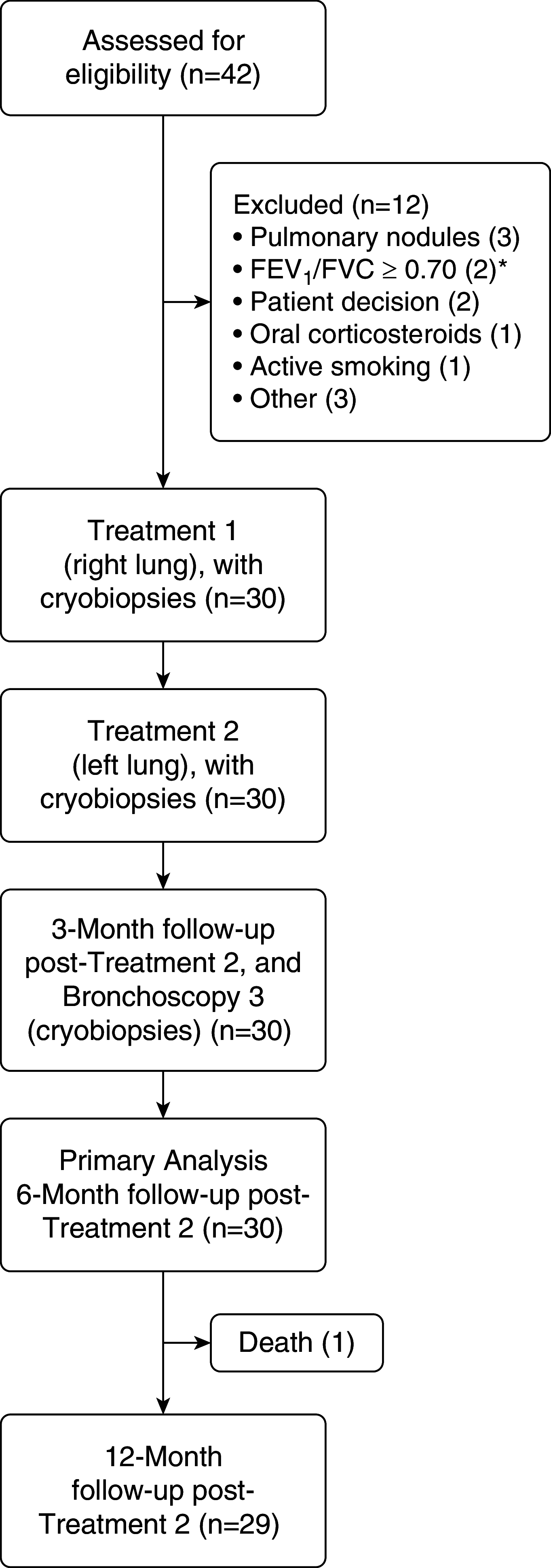
Rationale: Chronic bronchitis (CB) is characterized by productive cough with excessive mucus production, resulting in quality-of-life impairment and increased exacerbation risk. Bronchial rheoplasty uses an endobronchial catheter to apply nonthermal pulsed electrical fields to the airways. Preclinical studies have demonstrated epithelial ablation followed by regeneration of normalized epithelium.Objectives: To evaluate the feasibility, safety, and initial outcomes of bronchial rheoplasty in patients with CB.Methods: Pooled analysis of two separate studies enrolling 30 patients undergoing bilateral bronchial rheoplasty was conducted. Follow-up through 6 months (primary outcome) and 12 months included assessment of adverse events, airway histology, and changes in symptoms using the Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Assessment Test and St. George's Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ).Measurements and Main Results: Bronchial rheoplasty was performed in all 30 patients (63% male; mean [SD] age, 67 [7.4]; mean [SD] postbronchodilator FEV1, 65% [21%]; mean [SD] COPD Assessment Test score 25.6 [7.1]; mean [SD] SGRQ score, 59.6 [15.3]). There were no device-related and four procedure-related serious adverse events through 6 months, and there were none thereafter through 12 months. The most frequent nonserious, device- and/or procedure-related event through 6 months was mild hemoptysis in 47% (14 of 30) patients. Histologically, the mean goblet cell hyperplasia score was reduced by a statistically significant amount (P < 0.001). Significant changes from baseline to 6 months in COPD Assessment Test (mean, -7.9; median, -8.0; P = 0.0002) and SGRQ (mean, -14.6; median, -7.2; P = 0.0002) scores were observed, with similar observations through 12 months.Conclusions: This study provides the first clinical evidence of the feasibility, safety, and initial outcomes of bronchial rheoplasty in symptomatic patients with CB.Clinical trial registered with www.anzctr.org.au (ACTRN 12617000330347) and clinicaltrials.gov (NCT03107494).
Keywords: lung diseases; bronchial diseases; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; obstructive; pulsed electric field; respiratory tract diseases.
Figures



Comment in
-
Epithelial Resurfacing: The Bronchial Skin Peel.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020 Sep 1;202(5):641-642. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202004-1097ED. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020. PMID: 32441988 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Vogelmeier CF, Criner GJ, Martinez FJ, Anzueto A, Barnes PJ, Bourbeau J, et al. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive lung disease 2017 report: GOLD executive summary. Eur Respir J. 2017;49:1700214. - PubMed
-
- Verra F, Escudier E, Lebargy F, Bernaudin JF, De Crémoux H, Bignon J. Ciliary abnormalities in bronchial epithelium of smokers, ex-smokers, and nonsmokers. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995;151:630–634. - PubMed
-
- Saetta M, Turato G, Baraldo S, Zanin A, Braccioni F, Mapp CE, et al. Goblet cell hyperplasia and epithelial inflammation in peripheral airways of smokers with both symptoms of chronic bronchitis and chronic airflow limitation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000;161:1016–1021. - PubMed
-
- Innes AL, Woodruff PG, Ferrando RE, Donnelly S, Dolganov GM, Lazarus SC, et al. Epithelial mucin stores are increased in the large airways of smokers with airflow obstruction. Chest. 2006;130:1102–1108. - PubMed
-
- Vestbo J, Prescott E, Lange P Copenhagen City Heart Study Group. Association of chronic mucus hypersecretion with FEV1 decline and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease morbidity. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996;153:1530–1535. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

