MCH Neurons Regulate Permeability of the Median Eminence Barrier
- PMID: 32407670
- PMCID: PMC7383232
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2020.04.020
MCH Neurons Regulate Permeability of the Median Eminence Barrier
Abstract
Melanin-concentrating hormone (MCH)-expressing neurons are key regulators of energy and glucose homeostasis. Here, we demonstrate that they provide dense projections to the median eminence (ME) in close proximity to tanycytes and fenestrated vessels. Chemogenetic activation of MCH neurons as well as optogenetic stimulation of their projections in the ME enhance permeability of the ME by increasing fenestrated vascular loops and enhance leptin action in the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus (ARC). Unbiased phosphoRiboTrap-based assessment of cell activation upon chemogenetic MCH neuron activation reveals MCH-neuron-dependent regulation of endothelial cells. MCH neurons express the vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA), and blocking VEGF-R signaling attenuates the leptin-sensitizing effect of MCH neuron activation. Our experiments reveal that MCH neurons directly regulate permeability of the ME barrier, linking the activity of energy state and sleep regulatory neurons to the regulation of hormone accessibility to the ARC.
Keywords: MCH neurons; VEGF; blood brain barrier; body weight; energy homeostasis; feeding; fenestrated vessels; hypothalamus; leptin; median eminence; neuroendocrinology; obesity.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


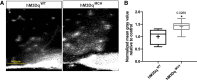
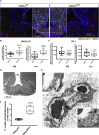
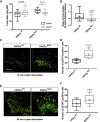


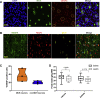
Comment in
-
A Novel Neurovascular Liaison Governing the Blood-Brain Barrier.Neuron. 2020 Jul 22;107(2):205-207. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2020.06.024. Neuron. 2020. PMID: 32702343 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bittencourt J.C. Anatomical organization of the melanin-concentrating hormone peptide family in the mammalian brain. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2011;172:185–197. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

