Production of Raw Starch-Digesting Amylolytic Preparation in Yarrowia lipolytica and Its Application in Biotechnological Synthesis of Lactic Acid and Ethanol
- PMID: 32408498
- PMCID: PMC7284447
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms8050717
Production of Raw Starch-Digesting Amylolytic Preparation in Yarrowia lipolytica and Its Application in Biotechnological Synthesis of Lactic Acid and Ethanol
Abstract
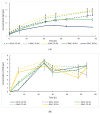
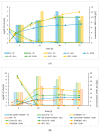
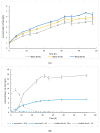
Sustainable economy drives increasing demand for raw biomass-decomposing enzymes. Microbial expression platforms exploited as cellular factories of such biocatalysts meet requirements of large-volume production. Previously, we developed Yarrowia lipolytica recombinant strains able to grow on raw starch of different plant origin. In the present study, we used the most efficient amylolytic strain as a microbial cell factory of raw-starch-digesting (RSD) amylolytic preparation composed of two enzymes. The RSD-preparation was produced in fed-batch bioreactor cultures. Concentrated and partly purified preparation was then tested in simultaneous saccharification and fermentation (SSF) processes with thermotolerant Kluyveromyces marxianus for ethanol production and Lactobacillus plantarum for production of lactic acid. These processes were conducted as a proof-of-concept that application of the novel RSD-preparation supports sufficient starch hydrolysis enabling microbial growth and production of targeted molecules, as the selected strains were confirmed to lack amylolytic activity. Doses of the preparation and thermal conditions were individually adjusted for the two processes. Additionally, ethanol production was tested under different aeration strategies; and lactic acid production process was tested in thermally pre-treated substrate, as well. Conducted studies demonstrated that the novel RSD-preparation provides satisfactory starch hydrolyzing activity for ethanol and lactic acid production from starch by non-amylolytic microorganisms.
Keywords: Kluyveromyces marxianus; Lactobacillus plantarum; Yarrowia lipolytica; ethanol; heterologous protein production; lactic acid; protein expression platform; raw starch; raw starch digesting enzymes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Evaluation of a recombinant insect-derived amylase performance in simultaneous saccharification and fermentation process with industrial yeasts.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016 Mar;100(6):2693-707. doi: 10.1007/s00253-015-7098-8. Epub 2015 Nov 7. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 26545757 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of heterologous α-amylase production in two expression platforms dedicated for Yarrowia lipolytica: commercial Po1g-pYLSC (php4d) and custom-made A18-pYLTEF (pTEF).Yeast. 2016 May;33(5):165-81. doi: 10.1002/yea.3149. Epub 2016 Jan 27. Yeast. 2016. PMID: 26694961
-
Efficient hydrolysis of raw starch and ethanol fermentation: a novel raw starch-digesting glucoamylase from Penicillium oxalicum.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2016 Oct 18;9:216. doi: 10.1186/s13068-016-0636-5. eCollection 2016. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2016. PMID: 27777618 Free PMC article.
-
Amylolytic bacterial lactic acid fermentation - a review.Biotechnol Adv. 2008 Jan-Feb;26(1):22-34. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2007.07.004. Epub 2007 Jul 31. Biotechnol Adv. 2008. PMID: 17884326 Review.
-
Consolidated bioprocessing of raw starch to ethanol by Saccharomyces cerevisiae: Achievements and challenges.Biotechnol Adv. 2020 Sep-Oct;42:107579. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2020.107579. Epub 2020 Jun 25. Biotechnol Adv. 2020. PMID: 32593775 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Cellulose-Degrading Bacteria and Assessment of Their Potential Value for the Production of Bioethanol from Coconut Oil Cake Waste.Microorganisms. 2024 Jan 24;12(2):240. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12020240. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38399644 Free PMC article.
-
Production of Lactate by Metabolically Engineered Scheffersomyces stipitis.J Fungi (Basel). 2025 May 27;11(6):413. doi: 10.3390/jof11060413. J Fungi (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40558924 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Singh H., Soni S.K. Production of starch-gel digesting amyloglucosidase by Aspergillus oryzae HS-3 in solid state fermentation. Process Biochem. 2001;37:453–459. doi: 10.1016/S0032-9592(01)00238-2. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

