Molecular Mechanisms of Heat Shock Factors in Cancer
- PMID: 32408596
- PMCID: PMC7290425
- DOI: 10.3390/cells9051202
Molecular Mechanisms of Heat Shock Factors in Cancer
Abstract
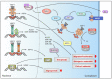
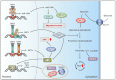
Malignant transformation is accompanied by alterations in the key cellular pathways that regulate development, metabolism, proliferation and motility as well as stress resilience. The members of the transcription factor family, called heat shock factors (HSFs), have been shown to play important roles in all of these biological processes, and in the past decade it has become evident that their activities are rewired during tumorigenesis. This review focuses on the expression patterns and functions of HSF1, HSF2, and HSF4 in specific cancer types, highlighting the mechanisms by which the regulatory functions of these transcription factors are modulated. Recently developed therapeutic approaches that target HSFs are also discussed.
Keywords: carcinogenesis; heat shock factor; heat shock response; proteotoxic stress; transcription.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ritossa F. A new puffing pattern induced by temperature shock and DNP in Drosophila. Experientia. 1962;18:571–573. doi: 10.1007/BF02172188. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

