Therapeutic Emergence of Rhein as a Potential Anticancer Drug: A Review of Its Molecular Targets and Anticancer Properties
- PMID: 32408623
- PMCID: PMC7288145
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25102278
Therapeutic Emergence of Rhein as a Potential Anticancer Drug: A Review of Its Molecular Targets and Anticancer Properties
Abstract
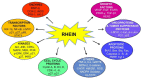
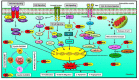
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), cancer is the second-highest cause of mortality in the world, and it kills nearly 9.6 million people annually. Besides the fatality of the disease, poor prognosis, cost of conventional therapies, and associated side-effects add more burden to patients, post-diagnosis. Therefore, the search for alternatives for the treatment of cancer that are safe, multi-targeted, effective, and cost-effective has compelled us to go back to ancient systems of medicine. Natural herbs and plant formulations are laden with a variety of phytochemicals. One such compound is rhein, which is an anthraquinone derived from the roots of Rheum spp. and Polygonum multiflorum. In ethnomedicine, these plants are used for the treatment of inflammation, osteoarthritis, diabetes, and bacterial and helminthic infections. Increasing evidence suggests that this compound can suppress breast cancer, cervical cancer, colon cancer, lung cancer, ovarian cancer, etc. in both in vitro and in vivo settings. Recent studies have reported that this compound modulates different signaling cascades in cancer cells and can prevent angiogenesis and progression of different types of cancers. The present review highlights the cancer-preventing and therapeutic properties of rhein based on the available literature, which will help to extend further research to establish the chemoprotective and therapeutic roles of rhein compared to other conventional drugs. Future pharmacokinetic and toxicological studies could support this compound as an effective anticancer agent.
Keywords: cancer; chemoprevention; chemotherapy; molecular targets; phytochemical; rhein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Devi Khwairakpam A., Monisha J., Roy N.K., Bordoloi D., Padmavathi G., Banik K., Khatoon E., Kunnumakkara A.B. Vietnamese coriander inhibits cell proliferation, survival and migration via suppression of Akt/mTOR pathway in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2019 doi: 10.1515/jbcpp-2019-0162. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

