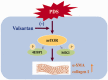
Valsartan ameliorates high glucose-induced peritoneal fibrosis by blocking mTORC1 signaling
- PMID: 32408765
- PMCID: PMC7427179
- DOI: 10.1177/1535370220919364
Valsartan ameliorates high glucose-induced peritoneal fibrosis by blocking mTORC1 signaling
Abstract
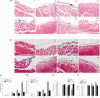
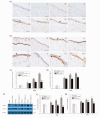
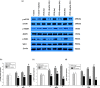
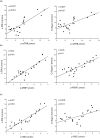
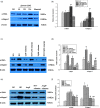
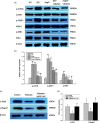
Our study provided new insight into the mechanism underlying the preservation of the peritoneum by valsartan. The results demonstrated that the mice receiving chronic high glucose (HG) peritoneal dialysis solution infusion showed a typical feature of peritoneal fibrosis (PF), as well as higher expression of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) and collagen I. In vitro, HG increased the protein expression of α-SMA and collagen I in a dose-dependent manner, while valsartan significantly ameliorated these pathological changes. Interestingly, there was a parallel decrease in the activity of mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) and the protein expression levels of α-SMA and collagen I upon treatment with valsartan in vivo and in vitro. Moreover, the mTOR agonist MHY1485 reversed the downregulation of α-SMA and collagen I in vitro, even in the presence of valsartan. Altogether, our findings reported for the first time that valsartan exerts a protective effect against HG-induced PF by inhibiting the activity of the mTORC1 pathway.
Keywords: Valsartan; extracellular matrix accumulation; high-glucose peritoneal dialysis solution; human peritoneal mesothelial cell; mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1; peritoneal fibrosis.
Figures
References
-
- Zhang Z, Jiang N, Ni Z. Strategies for preventing peritoneal fibrosis in peritoneal dialysis patients: new insights based on peritoneal inflammation and angiogenesis. Front Med 2017; 11:349–58 - PubMed
-
- Zhou Q, Bajo MA, Del Peso G, Yu X, Selgas R. Preventing peritoneal membrane fibrosis in peritoneal dialysis patients. Kidney Int 2016; 90:515–24 - PubMed
-
- Sun X, Wei W, Ren J, Liang Y, Wang M, Gui Y, Xue X, Li J, Dai C. Inhibition of 4E-BP1 phosphorylation promotes tubular cell escaping from G2/M arrest and ameliorates kidney fibrosis. Cell Signal 2019; 62:109331. - PubMed
-
- Woodcock HV, Eley JD, Guillotin D, Plate M, Nanthakumar CB, Martufi M, Peace S, Joberty G, Poeckel D, Good RB, Taylor AR, Zinn N, Redding M, Forty EJ, Hynds RE, Swanton C, Karsdal M, Maher TM, Bergamini G, Marshall RP, Blanchard AD, Mercer PF, Chambers RC. The mTORC1/4E-BP1 axis represents a critical signaling node during fibrogenesis. Nat Commun 2019; 10:6. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

