Engineering nanoparticles to reprogram radiotherapy and immunotherapy: recent advances and future challenges
- PMID: 32408880
- PMCID: PMC7227304
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-020-00629-y
Engineering nanoparticles to reprogram radiotherapy and immunotherapy: recent advances and future challenges
Abstract
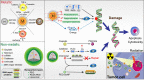
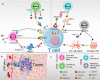
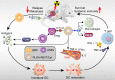
Nanoparticles (NPs) have been increasingly studied for radiosensitization. The principle of NPs radio-enhancement is to use high-atomic number NPs (e.g. gold, hafnium, bismuth and gadolinium) or deliver radiosensitizing substances, such as cisplatin and selenium. Nowadays, cancer immunotherapy is emerged as a promising treatment and immune checkpoint regulation has a potential property to improve clinical outcomes in cancer immunotherapy. Furthermore, NPs have been served as an ideal platform for immunomodulator system delivery. Owing to enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect, modified-NPs increase the targeting and retention of antibodies in target cells. The purpose of this review is to highlight the latest progress of nanotechnology in radiotherapy (RT) and immunotherapy, as well as combining these three strategies in cancer treatment. Overall, nanomedicine as an effective strategy for RT can significantly enhance the outcome of immunotherapy response and might be beneficial for clinical transformation.
Keywords: Immune checkpoint blockade therapy; Immunotherapy; Nanoparticles; Radiotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests
Figures
Similar articles
-
Advances of Nanomedicine in Radiotherapy.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Oct 21;13(11):1757. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13111757. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34834172 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineering Nanoparticles toward the Modulation of Emerging Cancer Immunotherapy.Adv Healthc Mater. 2021 Mar;10(5):e2000845. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202000845. Epub 2020 Aug 12. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021. PMID: 32790039 Review.
-
Nanotechnology platforms for cancer immunotherapy.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2020 Mar;12(2):e1590. doi: 10.1002/wnan.1590. Epub 2019 Nov 7. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2020. PMID: 31696664 Review.
-
Advances in engineering local drug delivery systems for cancer immunotherapy.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2020 Sep;12(5):e1632. doi: 10.1002/wnan.1632. Epub 2020 Apr 7. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32255276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanomedicine-based cancer immunotherapy: recent trends and future perspectives.Cancer Gene Ther. 2021 Sep;28(9):911-923. doi: 10.1038/s41417-021-00299-4. Epub 2021 Feb 8. Cancer Gene Ther. 2021. PMID: 33558704 Review.
Cited by
-
The Impact of Nanomedicine on Soft Tissue Sarcoma Treated by Radiotherapy and/or Hyperthermia: A Review.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jan 17;16(2):0. doi: 10.3390/cancers16020393. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38254881 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of Radiosensitizers in Cancer Radiotherapy.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Feb 12;16:1083-1102. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S290438. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 33603370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Applications of Magnetite Nanoparticles in Cancer Immunotherapies: Present Hallmarks and Future Perspectives.Front Immunol. 2021 Oct 4;12:701485. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.701485. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34675914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiation-induced tumor immune microenvironments and potential targets for combination therapy.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 May 19;8(1):205. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01462-z. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 37208386 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoparticle-Based Drug Delivery Systems Targeting Tumor Microenvironment for Cancer Immunotherapy Resistance: Current Advances and Applications.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Sep 21;14(10):1990. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14101990. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36297426 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lazarovits J, Chen YY, Sykes EA, Chan WC. Nanoparticle-blood interactions: the implications on solid tumour targeting. Chem Commun (Camb) 2015;51:2756–2767. - PubMed
-
- Rancoule C, Magne N, Vallard A, Guy JB, Rodriguez-Lafrasse C, Deutsch E, Chargari C. Nanoparticles in radiation oncology: from bench-side to bedside. Cancer Lett. 2016;375:256–262. - PubMed
-
- Zhao Z, Lou S, Hu Y, Zhu J, Zhang C. A nano-in-nano polymer-dendrimer nanoparticle-based nanosystem for controlled multidrug delivery. Mol Pharm. 2017;14:2697–2710. - PubMed
-
- El-Say KM, El-Sawy HS. Polymeric nanoparticles: promising platform for drug delivery. Int J Pharm. 2017;528:675–691. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

