Podoplanin is a useful prognostic marker and indicates better differentiation in lung squamous cell cancer patients? A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 32408907
- PMCID: PMC7227255
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-020-06936-9
Podoplanin is a useful prognostic marker and indicates better differentiation in lung squamous cell cancer patients? A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The CSC (cancer stem cell) markers often indicate poor prognosis and more cell invasion or migration of cancer patients. Podoplanin was assumed as a candidate CSC marker and predict poor prognosis among squamous cancers. Whereas, the prognostic value of podoplanin among lung squamous cancer (LUSC) patients remains controversial.
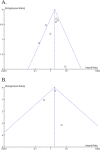
Methods: A search of databases including PubMed, Embase and Web of Science was performed. Eligible articles studying the prognostic significance of podoplanin were selected. Odds ratio and HR (hazard ratio) were used to assess the relationships between podoplanin and clinical characteristics, as well as to quantify its prognostic role. The heterogeneity was estimated by I2 Statistic and P values from sensitivity analysis. Begg's funnel plots were used to estimate possible publication bias.
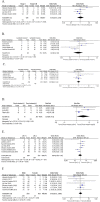
Results: 8 eligible studies containing 725 I-IV LUSC patients were included. Podoplanin expression showed no significant correlations with TNM stage, vascular invasion, lymphatic invasion, lymph node metastasis, pleural metastasis of tumor and gender of patients. However, podoplanin showed significant associations with better differentiation (pooled OR = 2.64, 95% CI 1.53-4.56, P = 0.0005, fixed effect) and better overall survival (HR = 2.14, 95% CI 1.45-3.15, P = 0.0001, fixed effect) and progression-free survival (HR = 1.73, 95% CI: 1.01-2.98, P = 0.05, fixed effect) of LUSC. Funnel plots illustrated no evidence of publication bias in our results.
Conclusions: Podoplanin could be a useful prognostic marker and indicates better differentiation for LUSC patients, and the value of PDPN expression as a marker for cancer stem cells in LUSC should be critically evaluated in future studies.
Keywords: Lung squamous cell carcinoma; Meta-analysis; PDPN protein; Prognosis; Stem cell marker.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Podoplanin expression is correlated with the prognosis of lung squamous cell carcinoma.Biomed Res. 2015;36(6):393-402. doi: 10.2220/biomedres.36.393. Biomed Res. 2015. PMID: 26700593
-
Podoplanin Expression in Cancer-associated Fibroblasts Predicts Poor Prognosis in Patients with Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Lung.Anticancer Res. 2017 Jan;37(1):207-213. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.11308. Anticancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28011493
-
Podoplanin-positive cancer-associated fibroblasts could have prognostic value independent of cancer cell phenotype in stage I lung squamous cell carcinoma: usefulness of combining analysis of both cancer cell phenotype and cancer-associated fibroblast phenotype.Chest. 2013 Apr;143(4):963-970. doi: 10.1378/chest.12-0913. Chest. 2013. PMID: 23081722
-
Prognostic value of TGF-β in lung cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2019 Jul 15;19(1):691. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5917-5. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31307405 Free PMC article.
-
The clinicopathologic impacts and prognostic significance of GLUT1 expression in patients with lung cancer: A meta-analysis.Gene. 2019 Mar 20;689:76-83. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.12.006. Epub 2018 Dec 12. Gene. 2019. PMID: 30552981 Review.
Cited by
-
Serum Podoplanin Levels as a Potential Biomarker for Diabetic Nephropathy Progression: A Cross-Sectional Study.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024 Dec 6;17:4701-4710. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S500608. eCollection 2024. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024. PMID: 39660339 Free PMC article.
-
Neoplastic synovial lining cells that coexpress podoplanin and CD90 overproduce CSF-1, driving tenosynovial giant cell tumor.J Orthop Res. 2022 Aug;40(8):1918-1925. doi: 10.1002/jor.25216. Epub 2021 Dec 2. J Orthop Res. 2022. PMID: 34855235 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Relevance of CD4+, CD8+ and FOXP3+ TILs in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Correlations with PD-L1 and Cancer Stem Cell Markers.Biomedicines. 2021 Jun 8;9(6):653. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9060653. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34201050 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of podoplanin expression in vulvar squamous cell carcinoma and stromal fibroblasts and its prognostic implications.Sci Rep. 2025 Jun 20;15(1):20224. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-06908-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40542163 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Seymour L, Le Teuff G, Brambilla E, Shepherd FA, Soria J-C, Kratzke R, et al. LACE-Bio: Validation of Predictive and/or Prognostic Immunohistochemistry/Histochemistry-based Biomarkers in Resected Non–small-cell Lung Cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 2019;20(2):66–73. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2018.10.001. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

