Genome-Wide Association Studies of CKD and Related Traits
- PMID: 32409295
- PMCID: PMC7646230
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.00020120
Genome-Wide Association Studies of CKD and Related Traits
Abstract
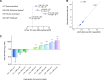
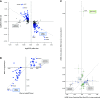
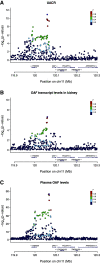
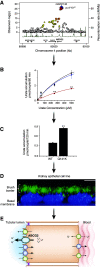
The past few years have seen major advances in genome-wide association studies (GWAS) of CKD and kidney function-related traits in several areas: increases in sample size from >100,000 to >1 million, enabling the discovery of >250 associated genetic loci that are highly reproducible; the inclusion of participants not only of European but also of non-European ancestries; and the use of advanced computational methods to integrate additional genomic and other unbiased, high-dimensional data to characterize the underlying genetic architecture and prioritize potentially causal genes and variants. Together with other large-scale biobank and genetic association studies of complex traits, these GWAS of kidney function-related traits have also provided novel insight into the relationship of kidney function to other diseases with respect to their genetic associations, genetic correlation, and directional relationships. A number of studies also included functional experiments using model organisms or cell lines to validate prioritized potentially causal genes and/or variants. In this review article, we will summarize these recent GWAS of CKD and kidney function-related traits, explain approaches for downstream characterization of associated genetic loci and the value of such computational follow-up analyses, and discuss related challenges along with potential solutions to ultimately enable improved treatment and prevention of kidney diseases through genetics.
Keywords: Biological Specimen Banks; Cell Line; Chronic; Follow-Up Studies; Genetic Association Studies; Genetic Loci; Genome; Genome-Wide Association Study; Genomics; Kidney Genomics Series; Multifactorial Inheritance; Renal Insufficiency; Sample Size; chronic kidney disease; genetic renal disease.
Copyright © 2020 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures

References
-
- Wuttke M, Köttgen A: Insights into kidney diseases from genome-wide association studies. Nat Rev Nephrol 12: 549–562, 2016. - PubMed
-
- Devuyst O: Genetics of kidney diseases in 2017: Unveiling the genetic architecture of kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol 14: 80–82, 2018. - PubMed
-
- Rasouly HM, Groopman EE, Heyman-Kantor R, Fasel DA, Mitrotti A, Westland R, Bier L, Weng C, Ren Z, Copeland B, Krithivasan P, Chung WK, Sanna-Cherchi S, Goldstein DB, Gharavi AG: The burden of candidate pathogenic variants for kidney and genitourinary disorders emerging from exome sequencing. Ann Intern Med 170: 11–21, 2019. - PubMed
-
- Tam V, Patel N, Turcotte M, Bossé Y, Paré G, Meyre D: Benefits and limitations of genome-wide association studies. Nat Rev Genet 20: 467–484, 2019. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

