Cerebrovascular Disease in COVID-19
- PMID: 32409316
- PMCID: PMC7357639
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A6588
Cerebrovascular Disease in COVID-19
Abstract
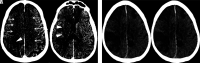
Coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19) is a pandemic originating in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. Early reports suggest that there are neurologic manifestations of COVID-19, including acute cerebrovascular disease. We report a case of COVID-19 with acute ischemic stroke. To our knowledge, this is the first reported case of COVID-19-related cerebral infarcts that includes brain imaging at multiple time points and CT angiography. There is a growing body of published evidence that complications of COVID-19 are not limited to the pulmonary system. Neuroradiologists should be aware of a wide range of neurologic manifestations, including cerebrovascular disease.
© 2020 by American Journal of Neuroradiology.
Figures

Comment in
-
Acute Common Carotid Artery Bifurcation Thrombus: An Emerging Pattern of Acute Strokes in Patients with COVID-19?AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2020 Aug;41(8):E65-E66. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A6657. Epub 2020 Jul 2. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2020. PMID: 32616583 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Reply.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2020 Aug;41(8):E64. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A6686. Epub 2020 Jul 9. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2020. PMID: 32646949 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Occam's Razor, Stroke, and COVID-19.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2020 Aug;41(8):E62-E63. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A6656. Epub 2020 Jul 9. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2020. PMID: 32646950 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Report of the WHO-China joint mission on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). February 16–24, 2020. https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/who-china-joint-mi.... Accessed April 15, 2020
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
