Shared and Independent Genetic Basis of Resistance to Bt Toxin Cry2Ab in Two Strains of Pink Bollworm
- PMID: 32409635
- PMCID: PMC7224296
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-64811-w
Shared and Independent Genetic Basis of Resistance to Bt Toxin Cry2Ab in Two Strains of Pink Bollworm
Abstract
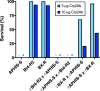
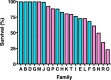
Evolution of pest resistance threatens the benefits of crops genetically engineered to produce insecticidal proteins from Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt). Field populations of the pink bollworm (Pectinophora gossypiella), a global pest of cotton, have evolved practical resistance to transgenic cotton producing Bt toxin Cry2Ab in India, but not in the United States. Previous results show that recessive mutations disrupting an autosomal ATP-binding cassette gene (PgABCA2) are associated with pink bollworm resistance to Cry2Ab in field-selected populations from India and in one lab-selected strain from the United States (Bt4-R2). Here we discovered that an independently derived, lab-selected Cry2Ab-resistant pink bollworm strain from the United States (BX-R) also harbors mutations that disrupt PgABCA2. Premature stop codons introduced by mis-splicing of PgABCA2 pre-mRNA were prevalent in field-selected larvae from India and in both lab-selected strains. The most common mutation in field-selected larvae from India was also detected in both lab-selected strains. Results from interstrain crosses indicate BX-R has at least one additional mechanism of resistance to Cry2Ab that does not involve PgABCA2 and is not completely recessive or autosomal. We conclude that recessive mutations disrupting PgABCA2 are the primary, but not the only, mechanism of resistance to Cry2Ab in pink bollworm.
Conflict of interest statement
This is a cooperative investigation between USDA ARS and the University of Arizona, with J.A.F., Y.C., and B.E.T. receiving funding from USDA National Institute of Food and Agriculture (Agriculture and Food Research Initiative Program Grant #2018-67013-27821) and Corteva Agriscience (agreement #58-3K95-4-1666) to support this work. D.L., G.C.U, and A.J.Y declare no potential conflict of interest. J.A.F. is coauthor of a patent “Cadherin Receptor Peptide for Potentiating Bt Biopesticides” (patent numbers: US20090175974A1, US8354371, WO2009067487A2, WO2009067487A3). B.E.T. is a coauthor of a patent on modified Bt toxins, “Suppression of Resistance in Insects to
Figures

Similar articles
-
CRISPR-mediated mutations in the ABC transporter gene ABCA2 confer pink bollworm resistance to Bt toxin Cry2Ab.Sci Rep. 2021 May 17;11(1):10377. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-89771-7. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34001946 Free PMC article.
-
ABC transporter mis-splicing associated with resistance to Bt toxin Cry2Ab in laboratory- and field-selected pink bollworm.Sci Rep. 2018 Sep 10;8(1):13531. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-31840-5. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30202031 Free PMC article.
-
Similar genetic basis of resistance to Bt toxin Cry1Ac in Boll-selected and diet-selected strains of pink bollworm.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e35658. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035658. Epub 2012 Apr 18. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22530065 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Genetic Basis of Lab- and Field-Selected Bt Resistance in Pink Bollworm.Insects. 2023 Feb 17;14(2):201. doi: 10.3390/insects14020201. Insects. 2023. PMID: 36835770 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early detection of field-evolved resistance to Bt cotton in China: cotton bollworm and pink bollworm.J Invertebr Pathol. 2012 Jul;110(3):301-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2012.04.008. Epub 2012 Apr 16. J Invertebr Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22537835 Review.
Cited by
-
Cadherin Is a Binding Protein but Not a Functional Receptor of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry2Ab in Helicoverpa armigera.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023 Jul 26;89(7):e0062523. doi: 10.1128/aem.00625-23. Epub 2023 Jun 28. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37378519 Free PMC article.
-
Knockout of ABC transporter gene ABCA2 confers resistance to Bt toxin Cry2Ab in Helicoverpa zea.Sci Rep. 2022 Oct 6;12(1):16706. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-21061-2. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36202979 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR-mediated mutations in the ABC transporter gene ABCA2 confer pink bollworm resistance to Bt toxin Cry2Ab.Sci Rep. 2021 May 17;11(1):10377. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-89771-7. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34001946 Free PMC article.
-
Chromosome-scale genome assembly of the pink bollworm, Pectinophora gossypiella, a global pest of cotton.G3 (Bethesda). 2023 Apr 11;13(4):jkad040. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkad040. G3 (Bethesda). 2023. PMID: 36790801 Free PMC article.
-
Streamlined phage display library protocols for identification of insect gut binding peptides highlight peptide specificity.Curr Res Insect Sci. 2021 Feb 18;1:100012. doi: 10.1016/j.cris.2021.100012. eCollection 2021. Curr Res Insect Sci. 2021. PMID: 36003592 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ISAAA. Global Status of Commercialized Biotech/GM Crops in 2018: Biotech Crops Continue to Help Meet the Challenges of Increased Population and Climate Change. ISAAA Brief No. 54 (ISAAA: Ithaca, NY, 2018).
-
- Hutchison, W. D. et al. Areawide suppression of European corn borer with Bt maize reaps savings to non-Bt maize growers. Science330, 222–225, 10.1126/science.1190242 (2010). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

