Prediction of the Development of Pulmonary Fibrosis Using Serial Thin-Section CT and Clinical Features in Patients Discharged after Treatment for COVID-19 Pneumonia
- PMID: 32410413
- PMCID: PMC7231610
- DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2020.0215
Prediction of the Development of Pulmonary Fibrosis Using Serial Thin-Section CT and Clinical Features in Patients Discharged after Treatment for COVID-19 Pneumonia
Abstract
Objective: To identify predictors of pulmonary fibrosis development by combining follow-up thin-section CT findings and clinical features in patients discharged after treatment for COVID-19.
Materials and methods: This retrospective study involved 32 confirmed COVID-19 patients who were divided into two groups according to the evidence of fibrosis on their latest follow-up CT imaging. Clinical data and CT imaging features of all the patients in different stages were collected and analyzed for comparison.
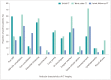
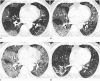
Results: The latest follow-up CT imaging showed fibrosis in 14 patients (male, 12; female, 2) and no fibrosis in 18 patients (male, 10; female, 8). Compared with the non-fibrosis group, the fibrosis group was older (median age: 54.0 years vs. 37.0 years, p = 0.008), and the median levels of C-reactive protein (53.4 mg/L vs. 10.0 mg/L, p = 0.002) and interleukin-6 (79.7 pg/L vs. 11.2 pg/L, p = 0.04) were also higher. The fibrosis group had a longer-term of hospitalization (19.5 days vs. 10.0 days, p = 0.001), pulsed steroid therapy (11.0 days vs. 5.0 days, p < 0.001), and antiviral therapy (12.0 days vs. 6.5 days, p = 0.012). More patients on the worst-state CT scan had an irregular interface (59.4% vs. 34.4%, p = 0.045) and a parenchymal band (71.9% vs. 28.1%, p < 0.001). On initial CT imaging, the irregular interface (57.1%) and parenchymal band (50.0%) were more common in the fibrosis group. On the worst-state CT imaging, interstitial thickening (78.6%), air bronchogram (57.1%), irregular interface (85.7%), coarse reticular pattern (28.6%), parenchymal band (92.9%), and pleural effusion (42.9%) were more common in the fibrosis group.
Conclusion: Fibrosis was more likely to develop in patients with severe clinical conditions, especially in patients with high inflammatory indicators. Interstitial thickening, irregular interface, coarse reticular pattern, and parenchymal band manifested in the process of the disease may be predictors of pulmonary fibrosis. Irregular interface and parenchymal band could predict the formation of pulmonary fibrosis early.
Keywords: COVID-19; Clinical characteristic; Computed tomography; Fibrosis; Follow-up; Prediction.
Copyright © 2020 The Korean Society of Radiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

Comment in
-
Pulmonary Fibrosis Due to COVID-19 Pneumonia.Korean J Radiol. 2020 Nov;21(11):1273-1275. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2020.0707. Epub 2020 Jul 17. Korean J Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32729265 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Lee N, Hui D, Wu A, Chan P, Cameron P, Joynt GM, et al. A major outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome in Hong Kong. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1986–1994. - PubMed
-
- Lew TW, Kwek TK, Tai D, Earnest A, Loo S, Singh K, et al. Acute respiratory distress syndrome in critically ill patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. JAMA. 2003;290:374–380. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

