Prognostic implication and functional exploration for microRNA-20a as a molecular biomarker of gastrointestinal cancer
- PMID: 32410584
- PMCID: PMC7227208
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-020-06875-5
Prognostic implication and functional exploration for microRNA-20a as a molecular biomarker of gastrointestinal cancer
Abstract
Background: It is generally accepted that microRNA-20a (miR-20a) is aberrantly expressed in gastrointestinal cancer (GIC), and may be associated with the prognosis of GIC patients. Nevertheless, the clinical prognostic value of miR-20a expression in GIC remains controversial.
Methods: We first conducted a comprehensive literature search of the clinical data and pooled them for evidence in assessing prognostic significance of miR-20a expression in GIC. Afterwards, we applied some bioinformatic analysis methods to explore the biological function of miR-20a and explain why miR-20a could act as an effective biomarker.
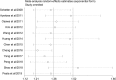
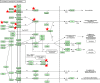
Results: The pooled results showed that enhanced miR-20a expression was significantly associated with poor survival in GIC patients (HR: 1.36; 95%CI: 1.21-1.52; P < 0.001). According to the subgroup analysis, the ethnicity, cancer type, sample source, and sample size may have an impact on the predictive roles for miR-20a. The gene ontologies enriched by the predicted miR-20a targets were highly associated with some important biological processes, cell components and molecular functions. Moreover, a series of prominent pathways linked with GIC carcinogenesis were identified. Ultimately, the crucial targets and modules were identified by constructing the protein-protein interaction network of miR-20a targets, which were highly associated with the initiation and progression of GIC according to previous molecular biology experiments.
Conclusions: Our results indicated that high expression of miR-20a may be a credible indicator of worse prognosis in GIC. Further studies involving biological experiments and larger sample sizes should be performed to validate these findings.
Keywords: Function exploration; Gastrointestinal cancer; Prognosis prediction; microRNA-20a.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no competing interest.
Figures






References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

