Long-term safety and tolerability of atabecestat (JNJ-54861911), an oral BACE1 inhibitor, in early Alzheimer's disease spectrum patients: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study and a two-period extension study
- PMID: 32410694
- PMCID: PMC7227237
- DOI: 10.1186/s13195-020-00614-5
Long-term safety and tolerability of atabecestat (JNJ-54861911), an oral BACE1 inhibitor, in early Alzheimer's disease spectrum patients: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study and a two-period extension study
Abstract
Background: Atabecestat, a potent brain-penetrable inhibitor of BACE1 activity that reduces CSF amyloid beta (Aβ), was developed for oral treatment for Alzheimer's disease (AD). The long-term safety and effect of atabecestat on cognitive performance in participants with predementia AD in two phase 2 studies were assessed.
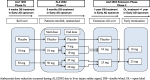
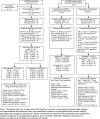
Methods: In the placebo-controlled double-blind parent ALZ2002 study, participants aged 50 to 85 years were randomized (1:1:1) to placebo or atabecestat 10 or 50 mg once daily (later reduced to 5 and 25 mg) for 6 months. Participants entered ALZ2004, a 12-month treatment extension with placebo or atabecestat 10 or 25 mg, followed by an open-label phase. Safety, changes in CSF biomarker levels, brain volume, and effects on cognitive performance were assessed.
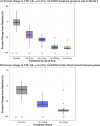
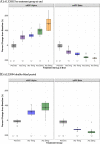
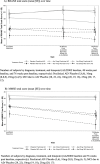
Results: Of 114 participants randomized in ALZ2002, 99 (87%) completed, 90 entered the ALZ2004 double-blind phase, and 77 progressed to the open-label phase. CSF Aβ fragments and sAPPβ were reduced dose-proportionately. Decreases in whole brain and hippocampal volumes were greater in participants with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) due to AD than in preclinical AD, but were not affected by treatment. In ALZ2004, change from baseline in RBANS trended toward worse scores for atabecestat versus placebo. Elevated liver enzyme adverse events reported in 12 participants on atabecestat resulted in dosage modification and increased frequency of safety monitoring. Treatment discontinuation normalized ALT or AST in all except one with pretreatment elevation, which remained mildly elevated. No case met ALT/AST > 3× ULN and total bilirubin > 2× ULN (Hy's law).
Conclusion: Atabecestat was associated with trend toward declines in cognition, and elevation of liver enzymes.
Trial registration: ALZ2002: ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT02260674, registered October 9, 2014; ALZ2004: ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT02406027, registered April 1, 2015.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Amyloid; Atabecestat; Aβ; BACE1 inhibitor; Cognition; Liver enzyme elevation; Predementia.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors, except Dr. Engelborghs, report personal fees (current or former employment) from Janssen Research & Development, a Division of Janssen Pharmaceutica NV, Beerse, Belgium, or Janssen Research & Development, LLC, Raritan, NJ, USA, or Janssen Research and Development LLC, Titusville, NJ, USA, and all own stock/stock options in the company.
Dr. Streffer is a former employee of Janssen Pharmaceutica NV and is currently affiliated with UCB Biopharma, Belgium, and with a research advisory role at Reference Center for Biological Markers of Dementia (BIODEM), Institute Born-Bunge, University of Antwerp, Antwerp, Belgium, and collects no consulting fees and receives no research funding.
Dr. Tesseur is a former employee of Janssen Pharmaceutica NV and is currently affiliated with UCB Biopharma, Belgium, and has nothing to disclose.
Dr. Tritsmans is a former employee of Janssen Pharmaceutica NV and reports no disclosures.
Dr. Engelborghs is employed at the Department of Biomedical Sciences, University of Antwerp, 2610 Antwerp, and at the Department of Neurology and Center for Neurosciences, UZ Brussel, and Vrije Universiteit Brussel (VUB), Brussels, Belgium, and reports research funding from Janssen Pharmaceutica NV and ADx Neurosciences (paid to institution).
Figures
References
-
- Timmers M, Van Broeck B, Ramael S, Slemmon J, De Waepenaert K, Russu A, Bogert JM, Stieltjes H, Shaw LM, Engelborghs S, Moechars D, Mercken M, Liu E, Sinha V, Kemp J, Van Nueten L, Tritsmans L, Streffer JR. Profiling the dynamics of CSF and plasma Aβ reduction after treatment with JNJ-54861911, a potent oral BACE inhibitor. Alzheimers Dement. 2016;2:202–212. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Timmers M, Streffer JR, Russu A, Tominaga Y, Shimizu H, Shiraishi A, et al. Pharmacodynamics of atabecestat (JNJ-54861911), an oral BACE1 inhibitor in patients with early Alzheimer’s disease: randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2018;10:85. doi: 10.1186/s13195-018-0415-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

