Recommendations for Developing Support Tools With People Suffering From Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Co-Design and Pilot Testing of a Mobile Health Prototype
- PMID: 32410730
- PMCID: PMC7260664
- DOI: 10.2196/16289
Recommendations for Developing Support Tools With People Suffering From Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Co-Design and Pilot Testing of a Mobile Health Prototype
Abstract
Background: Gaps exist between developers, commissioners, and end users in terms of the perceived desirability of different features and functionalities of mobile apps.
Objective: The objective of this study was to co-design a prototype mobile app for people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). We present lessons learned and recommendations from working on a large project with various stakeholders to develop a mobile app for patients with COPD.
Methods: We adopted a user-centered, participatory approach to app development. Following a series of focus groups and interviews to capture requirements, we developed a prototype app designed to enable daily symptom recording (experience sampling). The prototype was tested in a usability study applying the think aloud protocol with people with COPD. It was then released via the Android app store, and experience sampling data and event data were captured to gather further usability data.
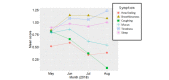
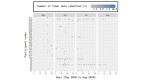
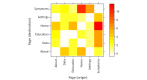
Results: A total of 5 people with COPD participated in the pilot study. Identified themes include familiarity with technology, appropriate levels for feeding back information, and usability issues such as manual dexterity. Moreover, 37 participants used the app over a 4-month period (median age 47 years). The symptoms most correlated to perceived well-being were tiredness (r=0.61; P<.001) and breathlessness (r=0.59; P<.001).
Conclusions: Design implications for COPD apps include the need for clearly labeled features (rather than relying on colors or symbols that require experience using smartphones), providing weather information, and using the same terminology as health care professionals (rather than simply lay terms). Target users, researchers, and developers should be involved at every stage of app development, using an iterative approach to build a prototype app, which should then be tested in controlled settings as well as in the wild (ie, when deployed and used in real-world settings) over longer periods.
Keywords: app design; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; ecological momentary assessment; mHealth; mobile phone.
©Alan Davies, Julia Mueller, Jean Hennings, Ann-Louise Caress, Caroline Jay. Originally published in JMIR Human Factors (http://humanfactors.jmir.org), 15.05.2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures





References
-
- Lung disease in the UK | British Lung Foundation. 2018. [2018-03-20]. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Statistics https://statistics.blf.org.uk/copd .
-
- Sobnath DD, Philip N, Kayyali R, Nabhani-Gebara S, Pierscionek B, Vaes AW, Spruit MA, Kaimakamis E. Features of a mobile support app for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: literature review and current applications. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2017 Mar 20;5(2):e17. doi: 10.2196/mhealth.4951. https://mhealth.jmir.org/2017/2/e17/ v5i2e17 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. 2017. Dec 1, [2020-03-30]. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/chronic-obstructive-pul...
-
- Fletcher MJ, Upton J, Taylor-Fishwick J, Buist SA, Jenkins C, Hutton J, Barnes N, van der Molen T, Walsh JW, Jones P, Walker S. COPD uncovered: an international survey on the impact of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [COPD] on a working age population. BMC Public Health. 2011 Aug 1;11:612. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-11-612. https://bmcpublichealth.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1471-2458-11-612 1471-2458-11-612 - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

