An outbreak of severe Kawasaki-like disease at the Italian epicentre of the SARS-CoV-2 epidemic: an observational cohort study
- PMID: 32410760
- PMCID: PMC7220177
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31103-X
An outbreak of severe Kawasaki-like disease at the Italian epicentre of the SARS-CoV-2 epidemic: an observational cohort study
Abstract
Background: The Bergamo province, which is extensively affected by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) epidemic, is a natural observatory of virus manifestations in the general population. In the past month we recorded an outbreak of Kawasaki disease; we aimed to evaluate incidence and features of patients with Kawasaki-like disease diagnosed during the SARS-CoV-2 epidemic.
Methods: All patients diagnosed with a Kawasaki-like disease at our centre in the past 5 years were divided according to symptomatic presentation before (group 1) or after (group 2) the beginning of the SARS-CoV-2 epidemic. Kawasaki- like presentations were managed as Kawasaki disease according to the American Heart Association indications. Kawasaki disease shock syndrome (KDSS) was defined by presence of circulatory dysfunction, and macrophage activation syndrome (MAS) by the Paediatric Rheumatology International Trials Organisation criteria. Current or previous infection was sought by reverse-transcriptase quantitative PCR in nasopharyngeal and oropharyngeal swabs, and by serological qualitative test detecting SARS-CoV-2 IgM and IgG, respectively.
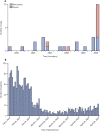
Findings: Group 1 comprised 19 patients (seven boys, 12 girls; aged 3·0 years [SD 2·5]) diagnosed between Jan 1, 2015, and Feb 17, 2020. Group 2 included ten patients (seven boys, three girls; aged 7·5 years [SD 3·5]) diagnosed between Feb 18 and April 20, 2020; eight of ten were positive for IgG or IgM, or both. The two groups differed in disease incidence (group 1 vs group 2, 0·3 vs ten per month), mean age (3·0 vs 7·5 years), cardiac involvement (two of 19 vs six of ten), KDSS (zero of 19 vs five of ten), MAS (zero of 19 vs five of ten), and need for adjunctive steroid treatment (three of 19 vs eight of ten; all p<0·01).
Interpretation: In the past month we found a 30-fold increased incidence of Kawasaki-like disease. Children diagnosed after the SARS-CoV-2 epidemic began showed evidence of immune response to the virus, were older, had a higher rate of cardiac involvement, and features of MAS. The SARS-CoV-2 epidemic was associated with high incidence of a severe form of Kawasaki disease. A similar outbreak of Kawasaki-like disease is expected in countries involved in the SARS-CoV-2 epidemic.
Funding: None.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Autoimmune and inflammatory diseases following COVID-19.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020 Aug;16(8):413-414. doi: 10.1038/s41584-020-0448-7. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 32499548 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokine Profile in an Adolescent With Pediatric Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome Temporally Related to COVID-19.Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2020 Aug;39(8):e213-e215. doi: 10.1097/INF.0000000000002802. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2020. PMID: 32677813 No abstract available.
-
Association between COVID-19 and Kawasaki-like disease in children is a topic that needs further investigation.Evid Based Nurs. 2021 Apr;24(2):35. doi: 10.1136/ebnurs-2020-103319. Epub 2020 Dec 1. Evid Based Nurs. 2021. PMID: 33262169 No abstract available.
-
COVID-19-induced Kawasaki disease.Nat Med. 2020 Dec;26(12):1807. doi: 10.1038/s41591-020-01163-y. Nat Med. 2020. PMID: 33288939 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ministero della Salute Nuovo coronavirus: cosa c'è da sapere. http://www.salute.gov.it/portale/nuovocoronavirus/
-
- Flaxman S, Mishra S, Gandy A. Estimating the number of infections and the impact of nonpharmaceutical interventions on COVID-19 in 11 European countries. https://www.imperial.ac.uk/mrc-global-infectious-disease-analysis/covid-...
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

