Cortical Circuit Dysfunction as a Potential Driver of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
- PMID: 32410944
- PMCID: PMC7201269
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00363
Cortical Circuit Dysfunction as a Potential Driver of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Abstract
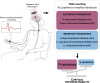
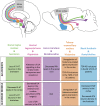
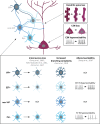
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a devastating neurodegenerative disease that affects selected cortical and spinal neuronal populations, leading to progressive paralysis and death. A growing body of evidences suggests that the disease may originate in the cerebral cortex and propagate in a corticofugal manner. In particular, transcranial magnetic stimulation studies revealed that ALS patients present with early cortical hyperexcitability arising from a combination of increased excitability and decreased inhibition. Here, we discuss the possibility that initial cortical circuit dysfunction might act as the main driver of ALS onset and progression, and review recent functional, imaging and transcriptomic studies conducted on ALS patients, along with electrophysiological, pathological and transcriptomic studies on animal and cellular models of the disease, in order to evaluate the potential cellular and molecular origins of cortical hyperexcitability in ALS.
Keywords: amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; cerebral cortex; extrinsic; hyperexcitability; intrinsic; network dysfunction.
Copyright © 2020 Brunet, Stuart-Lopez, Burg, Scekic-Zahirovic and Rouaux.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

