An Attempt to Polarize Human Neutrophils Toward N1 and N2 Phenotypes in vitro
- PMID: 32411122
- PMCID: PMC7198726
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00532
An Attempt to Polarize Human Neutrophils Toward N1 and N2 Phenotypes in vitro
Abstract
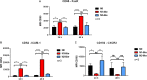
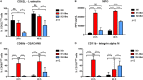
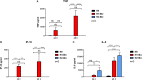
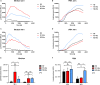
Neutrophils act as the first line of defense against invading pathogens. Although traditionally considered in context of their antimicrobial effector functions, the importance of tumor-associated neutrophils (TANs) in the development of cancer has become increasingly clear during the last decade. With regard to their high plasticity, neutrophils were shown to acquire an anti-tumorigenic N1 or a pro-tumorigenic N2 phenotype. Despite the urgent need to get a comprehensive understanding of the interaction of TANs with their tumor microenvironment, most studies still rely on murine tumor models. Here we present for the first time a polarization attempt to generate N1 and N2 neutrophils from primary human neutrophils in vitro. Our results underscore that N1-polarized neutrophils have a pro-inflammatory phenotype characterized among others by a higher level of intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-1 and high secretion of interferon (IFN)γ-induced protein 10 (IP-10)/C-X-C motif chemokine 10 (CXCL10) and tumor necrosis factor (TNF). Further, we demonstrate that neutrophils incubated under a tumor-mimicking in vitro environment show a high cell surface expression of C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 2 (CXCR2) and secrete high levels of interleukin (IL)-8. These findings suggest that it is feasible to polarize blood-derived primary human neutrophils toward N1- and N2-like phenotypes in vitro. Further, we hypothesized that the presence of anti-inflammatory neutrophil phenotype is not a phenomenon limited to cancer but also occurs when neutrophils are infected with intracellular pathogens. Indeed, our findings indicate that N2-polarized neutrophils exert a markedly decreased capacity to kill the protozoan parasite Leishmania donovani and therefore permit parasite persistence.
Keywords: Leishmania donovani; N1; N2; neutrophil heterogeneity; neutrophils; polarization; tumor-associated neutrophils; visceral leishmaniasis.
Copyright © 2020 Ohms, Möller and Laskay.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

