Anabolic Hormone Deficiencies in Heart Failure with Reduced or Preserved Ejection Fraction and Correlation with Plasma Total Antioxidant Capacity
- PMID: 32411227
- PMCID: PMC7199626
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/5798146
Anabolic Hormone Deficiencies in Heart Failure with Reduced or Preserved Ejection Fraction and Correlation with Plasma Total Antioxidant Capacity
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "Anabolic Hormone Deficiencies in Heart Failure with Reduced or Preserved Ejection Fraction and Correlation with Plasma Total Antioxidant Capacity".Int J Endocrinol. 2020 Oct 14;2020:5278040. doi: 10.1155/2020/5278040. eCollection 2020. Int J Endocrinol. 2020. PMID: 33178267 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: While anabolic hormone deficit is a common finding in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), few data are available in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF).
Methods: Blood samples were collected for metabolic (total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, creatinine, and glucose) and hormonal (IGF-1, DHEA-S, TSH, fT3, fT4, and T) determination, comparing 30 patients with HFpEF and 20 patients with HFrEF. Total antioxidant capacity was evaluated by using the spectrophotometric method using the latency time in the appearance of the radical species of a chromogen (LAG, sec) as a parameter proportional to antioxidant content of the sample. Echocardiographic parameters were also assessed in the two groups.
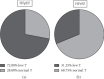
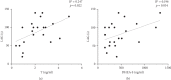
Results: A high prevalence of testosterone (32% in HFrEF and 72% in HFpEF, p < 0.05) and DHEA-S deficiencies was observed in HFpEF patients. Echocardiographic parameters did not correlate with hormone values. A significant direct correlation between T (r 2 = 0.25, p < 0.05) and DHEA-S (r 2 = 0.19, p < 0.05) with LAG was observed only in HFpEF.
Conclusion: Anabolic hormone deficiency is clearly shown in HFpEF, as already known in HFrEF. Although longitudinal studies are required to confirm the prognostic value of this observation, our data suggest different mechanisms in modulating antioxidants in the two conditions, with possible therapeutic implications.
Copyright © 2020 Antonio Mancini et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

