Effects of β2-adrenergic agonists on house dust mite-induced adhesion, superoxide anion generation, and degranulation of human eosinophils
- PMID: 32411580
- PMCID: PMC7203437
- DOI: 10.5415/apallergy.2020.10.e15
Effects of β2-adrenergic agonists on house dust mite-induced adhesion, superoxide anion generation, and degranulation of human eosinophils
Abstract
Background: Even in subjects who are not sensitized to house dust mite (HDM), allergic symptoms can be clinically aggravated by exposure to dust. We previously reported that Dermatophagoides farinae (Df), an important HDM, or Der f 1, a major allergen of Df, induced the effector functions of eosinophils, which may be an important mechanism for HDM-induced symptoms in nonsensitized patients. In a clinical setting, β2-adrenergic agonists, such as salbutamol and formoterol, are used for the treatment of asthma attacks or exacerbation to release the airway obstruction. Several reports have suggested that some β2-adrenergic agonists have an anti-inflammatory capacity.
Objective: In this study, we investigated whether β2-adrenergic agonist could modify the Df- or Der f 1-induced activation of eosinophils.
Methods: Blood eosinophils obtained from healthy donors were preincubated with either formoterol (1 μM), salbutamol (1 μM), or buffer control and then stimulated with Df extract (1 μg/mL) or Der f 1 (100 pg/mL). Eosinophil adhesion to intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-1 was measured using eosinophil peroxidase assays. Generation of superoxide anion (O2 -) was examined based on the superoxide dismutase-inhibitable reduction of cytochrome C. Eosinophil-derived neurotoxin (EDN) concentrations in cell media were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
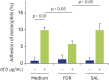
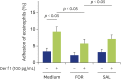
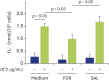
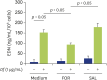
Results: Formoterol, but not salbutamol, suppressed the Df- or Der f 1-induced eosinophil adhesion to ICAM-1. Furthermore, formoterol, but not salbutamol, suppressed Df-induced O2 - generation or EDN release. Neither formoterol nor salbutamol suppressed spontaneous eosinophil adhesion, O2 - generation, or EDN release.
Conclusion: These findings suggested that formoterol, but not salbutamol, suppressed Df- or Der f 1-induced eosinophil activation when used at the same concentration. Therefore, formoterol could potentially be used for the treatment of bronchial asthma via both bronchodilation and anti-inflammatory effect.
Keywords: Beta2-adrenergic agonists; Der f 1; Eosinophils; Formoterol; House dust mite.
Copyright © 2020. Asia Pacific Association of Allergy, Asthma and Clinical Immunology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: KN received honoraria from AstraZeneca. KOD is employee of Torii Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. MN received honoraria from AstraZeneca and KYORIN Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. The other authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bochner BS, Undem BJ, Lichtenstein LM. Immunological aspects of allergic asthma. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:295–335. - PubMed
-
- Gleich GJ. Mechanisms of eosinophil-associated inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000;105:651–663. - PubMed
-
- Lambrecht BN. Dendritic cells and the regulation of the allergic immune response. Allergy. 2005;60:271–282. - PubMed
-
- Holgate ST. Innate and adaptive immune responses in asthma. Nat Med. 2012;18:673–683. - PubMed
-
- Jacquet A. The role of innate immunity activation in house dust mite allergy. Trends Mol Med. 2011;17:604–611. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
