Gender Differences in Patients With COVID-19: Focus on Severity and Mortality
- PMID: 32411652
- PMCID: PMC7201103
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2020.00152
Gender Differences in Patients With COVID-19: Focus on Severity and Mortality
Abstract
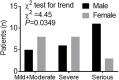
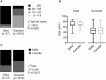
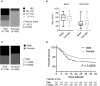
Objective: The recent outbreak of Novel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) is reminiscent of the SARS outbreak in 2003. We aim to compare the severity and mortality between male and female patients with COVID-19 or SARS. Study Design and Setting: We extracted the data from: (1) a case series of 43 hospitalized patients we treated, (2) a public data set of the first 37 cases of patients who died of COVID-19 and 1,019 patients who survived in China, and (3) data of 524 patients with SARS, including 139 deaths, from Beijing in early 2003. Results: Older age and a high number of comorbidities were associated with higher severity and mortality in patients with both COVID-19 and SARS. Age was comparable between men and women in all data sets. In the case series, however, men's cases tended to be more serious than women's (P = 0.035). In the public data set, the number of men who died from COVID-19 is 2.4 times that of women (70.3 vs. 29.7%, P = 0.016). In SARS patients, the gender role in mortality was also observed. The percentage of males were higher in the deceased group than in the survived group (P = 0.015). Conclusion: While men and women have the same prevalence, men with COVID-19 are more at risk for worse outcomes and death, independent of age.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS; SARS-CoV-2; female; gender; male; morbidity; mortality.
Copyright © 2020 Jin, Bai, He, Wu, Liu, Han, Liu and Yang.
Figures
Comment in
-
Why men's health?Postgrad Med. 2020 Dec;132(sup4):1-3. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2020.1805867. Epub 2020 Nov 6. Postgrad Med. 2020. PMID: 33156726 No abstract available.
References
-
- National Health Commission of PRC Daily Briefing on Novel Coronavirus Cases in China. (2020). Available online at: http://ennhcgovcn/2020-02/23/c_76779htm
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

