Air pollution reduction and mortality benefit during the COVID-19 outbreak in China
- PMID: 32411944
- PMCID: PMC7220178
- DOI: 10.1016/S2542-5196(20)30107-8
Air pollution reduction and mortality benefit during the COVID-19 outbreak in China
Figures
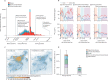
Comment in
-
Reduction in air pollution and attributable mortality due to COVID-19 lockdown.Lancet Planet Health. 2020 Jul;4(7):e268. doi: 10.1016/S2542-5196(20)30148-0. Lancet Planet Health. 2020. PMID: 32681895 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Reduction in air pollution and attributable mortality due to COVID-19 lockdown - Authors' reply.Lancet Planet Health. 2020 Jul;4(7):e269. doi: 10.1016/S2542-5196(20)30149-2. Lancet Planet Health. 2020. PMID: 32681896 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- China Ministry of Ecology and Environment Heavy air pollution in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei and surrounding areas and five experts answering the cause of pollution. 2020. http://www.mee.gov.cn/xxgk2018/xxgk/xxgk15/202002/t20200211_762584.html (in Chinese).
-
- Chen R, Yin P, Meng X, et al. Fine particulate air pollution and daily mortality. A nationwide analysis in 272 Chinese cities. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017;196:73–81. - PubMed
-
- Chen R, Yin P, Meng X, et al. Associations between ambient nitrogen dioxide and daily cause-specific mortality: evidence from 272 Chinese cities. Epidemiology. 2018;29:482–489. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

