Efficient targeted integration directed by short homology in zebrafish and mammalian cells
- PMID: 32412410
- PMCID: PMC7228771
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.53968
Efficient targeted integration directed by short homology in zebrafish and mammalian cells
Abstract
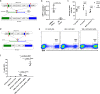
Efficient precision genome engineering requires high frequency and specificity of integration at the genomic target site. Here, we describe a set of resources to streamline reporter gene knock-ins in zebrafish and demonstrate the broader utility of the method in mammalian cells. Our approach uses short homology of 24-48 bp to drive targeted integration of DNA reporter cassettes by homology-mediated end joining (HMEJ) at high frequency at a double strand break in the targeted gene. Our vector series, pGTag (plasmids for Gene Tagging), contains reporters flanked by a universal CRISPR sgRNA sequence which enables in vivo liberation of the homology arms. We observed high rates of germline transmission (22-100%) for targeted knock-ins at eight zebrafish loci and efficient integration at safe harbor loci in porcine and human cells. Our system provides a straightforward and cost-effective approach for high efficiency gene targeting applications in CRISPR and TALEN compatible systems.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9; developmental biology; end joining; genetics; genomics; human; knock-in; pig fibroblasts; targeted integration; zebrafish.
© 2020, Wierson et al.
Conflict of interest statement
WW Interests in Lifengine and Lifengine Animal Health, JW, MA, CM, MT, TW, SK, MV, ML, KM, JL, ZM, AW, CM, JH, KK, CC, DB, BW, BM, DD, MM No competing interests declared, DW, SS, DC Shares in Recombinetics, Inc, SE Shares in Lifengine, and Lifengine Animal Health, KC Shares in Recombinetics, Inc, Lifengine and Lifengine Animal Health, JE JJE has a financial conflict of interest with Recombinetics, Inc; Immusoft, Inc; LifEngine and LifEngine Animal Technologies;
Figures










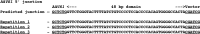
References
-
- Bedell VM, Wang Y, Campbell JM, Poshusta TL, Starker CG, Krug RG, Tan W, Penheiter SG, Ma AC, Leung AY, Fahrenkrug SC, Carlson DF, Voytas DF, Clark KJ, Essner JJ, Ekker SC. In vivo genome editing using a high-efficiency TALEN system. Nature. 2012;491:114–118. doi: 10.1038/nature11537. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

