Chronic cigarette smoke exposure triggers a vicious cycle of leukocyte and endothelial-mediated oxidant stress that results in vascular dysfunction
- PMID: 32412791
- PMCID: PMC7474439
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00657.2019
Chronic cigarette smoke exposure triggers a vicious cycle of leukocyte and endothelial-mediated oxidant stress that results in vascular dysfunction
Abstract
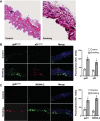
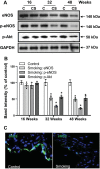
Although there is a strong association between cigarette smoking exposure (CSE) and vascular endothelial dysfunction (VED), the underlying mechanisms by which CSE triggers VED remain unclear. Therefore, studies were performed to define these mechanisms using a chronic mouse model of cigarette smoking (CS)-induced cardiovascular disease mirroring that in humans. C57BL/6 male mice were subjected to CSE for up to 48 wk. CSE impaired acetylcholine (ACh)-induced relaxation of aortic and mesenteric segments and triggered hypertension, with mean arterial blood pressure at 32 and 48 wk of exposure of 122 ± 6 and 135 ± 5 mmHg compared with 99 ± 4 and 102 ± 6 mmHg, respectively, in air-exposed mice. CSE led to monocyte activation with superoxide generation in blood exiting the pulmonary circulation. Macrophage infiltration with concomitant increase in NADPH oxidase subunits p22phox and gp91phox was seen in aortas of CS-exposed mice at 16 wk, with further increase out to 48 wk. Associated with this, increased superoxide production was detected that decreased with Nox inhibition. Tetrahydrobiopterin was progressively depleted in CS-exposed mice but not in air-exposed controls, resulting in endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) uncoupling and secondary superoxide generation. CSE led to a time-dependent decrease in eNOS and Akt expression and phosphorylation. Overall, CSE induces vascular monocyte infiltration with increased NADPH oxidase-mediated reactive oxygen species generation and depletes the eNOS cofactor tetrahydrobiopterin, uncoupling eNOS and triggering a vicious cycle of oxidative stress with VED and hypertension. Our study provides important insights toward understanding the process by which smoking contributes to the genesis of cardiovascular disease and identifies biomarkers predictive of disease.NEW & NOTEWORTHY In a chronic model of smoking-induced cardiovascular disease, we define underlying mechanisms of smoking-induced vascular endothelial dysfunction (VED). Smoking exposure triggered VED and hypertension and led to vascular macrophage infiltration with concomitant increase in superoxide and NADPH oxidase levels as early as 16 wk of exposure. This oxidative stress was accompanied by tetrahydrobiopterin depletion, resulting in endothelial nitric oxide synthase uncoupling with further superoxide generation triggering a vicious cycle of oxidative stress and VED.
Keywords: cigarette smoking; endothelial dysfunction; hypertension; inflammation; nitric oxide synthase uncoupling; reactive oxygen species; superoxide.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Electronic cigarette exposure causes vascular endothelial dysfunction due to NADPH oxidase activation and eNOS uncoupling.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2022 Apr 1;322(4):H549-H567. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00460.2021. Epub 2022 Jan 28. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35089811 Free PMC article.
-
The p47phox- and NADPH oxidase organiser 1 (NOXO1)-dependent activation of NADPH oxidase 1 (NOX1) mediates endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) uncoupling and endothelial dysfunction in a streptozotocin-induced murine model of diabetes.Diabetologia. 2012 Jul;55(7):2069-79. doi: 10.1007/s00125-012-2557-6. Epub 2012 May 2. Diabetologia. 2012. PMID: 22549734 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of Nox1 in vascular smooth muscle leads to impaired endothelium-dependent relaxation via eNOS uncoupling.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010 Sep;299(3):H673-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00242.2010. Epub 2010 Jul 16. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20639222 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms and consequences of endothelial nitric oxide synthase dysfunction in hypertension.J Hypertens. 2015 Jun;33(6):1128-36. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000000587. J Hypertens. 2015. PMID: 25882860 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Malfunction of vascular control in lifestyle-related diseases: mechanisms underlying endothelial dysfunction in the insulin-resistant state.J Pharmacol Sci. 2004 Dec;96(4):401-5. doi: 10.1254/jphs.fmj04006x4. Epub 2004 Dec 15. J Pharmacol Sci. 2004. PMID: 15599093 Review.
Cited by
-
Electronic cigarette exposure causes vascular endothelial dysfunction due to NADPH oxidase activation and eNOS uncoupling.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2022 Apr 1;322(4):H549-H567. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00460.2021. Epub 2022 Jan 28. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35089811 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic effect of secondhand smoke and apical periodontitis on lung tissue damage in rats.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 16;15(1):13088. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-97601-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40240867 Free PMC article.
-
A Mixture of Dietary Plant Sterols at Nutritional Relevant Serum Concentration Inhibits Extrinsic Pathway of Eryptosis Induced by Cigarette Smoke Extract.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 9;24(2):1264. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021264. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674779 Free PMC article.
-
[Beyond the plaque: immunological implications of risk factors in atherosclerosis].Arch Cardiol Mex. 2024 Oct 24;95(1):81-95. doi: 10.24875/ACM.23000246. Arch Cardiol Mex. 2024. PMID: 39447561 Free PMC article. Review. Spanish.
-
Cigarette Smoke-Induced Reactive Oxygen Species Formation: A Concise Review.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Sep 7;12(9):1732. doi: 10.3390/antiox12091732. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37760035 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abdelghany TM, El-Sherbiny GA, El-Mahdy MA, Zweier JL. Chronic cigarette smoke exposure impairs vascular endothelial function through a tetrahydrobiopterin-dependent mechanism (Abstract). 64th Tobacco Science Research Conference Hilton Head Island, SC, October 3-6, 2010, p. 48.
-
- Abdelghany TM, Ismail RS, Mansoor FA, Zweier JR, Lowe F, Zweier JL. Cigarette smoke constituents cause endothelial nitric oxide synthase dysfunction and uncoupling due to depletion of tetrahydrobiopterin with degradation of GTP cyclohydrolase. Nitric Oxide 76: 113–121, 2018. doi:10.1016/j.niox.2018.02.009. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Anderson CM, Lee CM, Saunders DP, Curtis A, Dunlap N, Nangia C, Lee AS, Gordon SM, Kovoor P, Arevalo-Araujo R, Bar-Ad V, Peddada A, Colvett K, Miller D, Jain AK, Wheeler J, Blakaj D, Bonomi M, Agarwala SS, Garg M, Worden F, Holmlund J, Brill JM, Downs M, Sonis ST, Katz S, Buatti JM. Phase IIb, randomized, double-blind trial of GC4419 versus placebo to reduce severe oral mucositis due to concurrent radiotherapy and cisplatin for head and neck cancer. J Clin Oncol 37: 3256–3265, 2019. doi:10.1200/JCO.19.01507. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Annuk M, Zilmer M, Lind L, Linde T, Fellström B. Oxidative stress and endothelial function in chronic renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol 12: 2747–2752, 2001. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

