Real-world efficacy, safety, and clinical outcomes of ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir ± dasabuvir ± ribavirin combination therapy in patients with hepatitis C virus genotype 1 or 4 infection: The Turkey experience experience
- PMID: 32412901
- PMCID: PMC7236650
- DOI: 10.5152/tjg.2020.19197
Real-world efficacy, safety, and clinical outcomes of ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir ± dasabuvir ± ribavirin combination therapy in patients with hepatitis C virus genotype 1 or 4 infection: The Turkey experience experience
Abstract
Background/aims: mbitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir (OMV/PTV/r) ± dasabuvir (DSV) ± ribavirin (RBV) combination has demonstrated excellent rates of sustained virologic response (SVR) and a very good safety profile in patients with the chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotype 1 or 4 infections. We aimed to investigate the effectiveness and safety of OMV/PTV/r ± DSV ± RBV combination regimen in a real-world clinical practice.
Materials and methods: Data from HCV genotype 1 and 4 patients treated with OMV/PTV/r ± DSV ± RBV (n=862) in 34 centers across Turkey between April 1, 2017 and August 31, 2018 were recorded in a large national database. Demographic, clinical, and virologic data were analyzed.
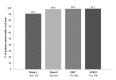
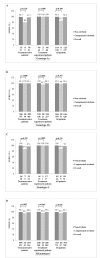
Results: The mean age of the patients was 55.63, and 430 patients (49.9%) were male. The majority had HCV genotype 1b infection (77.3%), and 66.2% were treatment-naïve. Non-cirrhosis was present at baseline in 789 patients (91.5%). SVR12 rate was 99.1% in all patients. Seven patients had virologic failure. No significant differences were observed in SVR12 according to HCV genotypes. HCV RNA was undetectable at treatment week 4 in 90.9%, at treatment week 8 in 98.5%, and at the end of treatment (EOT) in 98.9%. SVR12 ratio was significantly higher in the non-cirrhotic patients compared to that in the compensated cirrhotic patients. Rates of adverse events (AEs) in the patients was 59.7%.
Conclusion: The present real-life data of Turkey for the OBV/PTV/r ± DSV ± RBV treatment of patients with HCV genotype 1b, 1a, or 4 infection from 862 patients demonstrated high efficacy and a safety profile.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Aygen B, Nemirtürk N, Türker N, et al. Management of chronic hepatitis C virus infection: A consensus report of the Study Group for Viral Hepatitis of the Turkish Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases-2017 Update. Klimik J. 2017;30( Suppl 1):2–36. doi: 10.5152/kd.2017.12. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous