Esmolol inhibits inflammation and apoptosis in the intestinal tissue via the overexpression of NF-κB-p65 in the early stage sepsis rats
- PMID: 32412904
- PMCID: PMC7236645
- DOI: 10.5152/tjg.2020.19341
Esmolol inhibits inflammation and apoptosis in the intestinal tissue via the overexpression of NF-κB-p65 in the early stage sepsis rats
Abstract
Background/aims: Accumulating evidence reveals esmolol could protect the gut mucosa through the regulation of immune response and inflammation in patients with sepsis. However, its underlying mechanism is not fully understood.
Materials and methods: Diamine oxidase (DAO), intestinal fatty acid-binding protein (I-FABP), interleukin (IL)-6, and IL-10 in the plasma of rats were detected by ELISA assay. Western blotting was utilized to measure the expression levels of NF-kappa B-p65, Bcl-2, and cleaved caspase-3 in the intestinal tissues. The survival analysis was performed in each group.
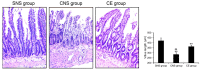
Results: The plasma levels of DAO and IL-10 levels were increased, whereas that of I-FABP and IL-6 were decreased in the sepsis rats after esmolol treatment, indicating that after the esmolol treatment, the intestinal inflammation and damages were remarkably reduced as compared to those in the normal saline treated sepsis rats. NF-κB-p65 and Bcl-2 were highly expressed, but cleaved caspase-3 showed lower expression in the esmolol treated groups. However, at the same time, we observed contrasting results in the normal saline treated group. Western blotting data indicated that the esmolol treatment inhibited the inflammation and apoptosis in the intestinal tissue due to the overexpression of NF-κB-p65 in the celiac sepsis rats. The survival analysis results indicate that the esmolol infusion should be used in the early stages sepsis rats.
Conclusion: Esmolol can suppress inflammation and apoptosis in the intestinal tissue via the overexpression of NF-kappa B-p65 in the early stage sepsis rats. kappa BEarly-stage use of esmolol might be an ideal treatment method for sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Esmolol upregulates the α7 nAChR/STAT3/NF-κB pathway by decreasing the ubiquitin and increasing the ChAT+CD4+ T lymphocyte to alleviate inflammation in septic cardiomyopathy.Int Immunopharmacol. 2025 Feb 20;148:114043. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2025.114043. Epub 2025 Jan 16. Int Immunopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39823793
-
[β1 receptor blocker decreases the myocardial inflammation in the sepsis adult rats through inhibition of TLR4/NF-ΚB signaling pathway].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019 Feb;31(2):193-197. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2019.02.014. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019. PMID: 30827308 Chinese.
-
[Ulinastatin protects intestinal mucosal barrier by inhibiting the activation of intestinal NLRP3 inflammasomes in septic rats].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2021 Feb;33(2):192-197. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20201208-00747. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2021. PMID: 33729139 Chinese.
-
[Effects of Na(+) /H(+) exchanger 1 inhibitor on intestinal injury of rats with burn sepsis and the mechanism].Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2017 Jun 20;33(6):349-354. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-2587.2017.06.013. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28648038 Chinese.
-
[Role of high mobility group box 1 in intestinal mucosal barrier injury in rat with sepsis induced by endotoxin].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020 Jul;32(7):803-807. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20200109-00126. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020. PMID: 32788013 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Esmolol increases the fecal abundance of Lactobacillus in a rat model of sepsis.Intensive Care Med Exp. 2024 Mar 4;12(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s40635-023-00589-1. Intensive Care Med Exp. 2024. PMID: 38433148 Free PMC article.
-
Beta-blockers in septic shock: What is new?J Intensive Med. 2022 Apr 3;2(3):150-155. doi: 10.1016/j.jointm.2022.01.004. eCollection 2022 Jul. J Intensive Med. 2022. PMID: 36789018 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of esmolol in sepsis: a meta-analysis based on randomized controlled trials.BMC Anesthesiol. 2024 Sep 12;24(1):326. doi: 10.1186/s12871-024-02714-3. BMC Anesthesiol. 2024. PMID: 39266951 Free PMC article.
-
Esmolol improves sepsis outcomes through cardiovascular and immune modulation.Front Pharmacol. 2025 May 12;16:1498227. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1498227. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40421209 Free PMC article.
-
Nalbuphine alleviates inflammation by down-regulating NF-κB in an acute inflammatory visceral pain rat model.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2022 Jun 1;23(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s40360-022-00573-7. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 35642022 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ikeh MAC, Fidel PL, Jr, Noverr MC. Identification of Specific Components of the Eicosanoid Biosynthetic and Signaling Pathway Involved in Pathological Inflammation during Intra-abdominal Infection with Candida albicans and Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 2018;86 doi: 10.1128/IAI.00144-18. pii: e00144–18. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
