Treatment of Overlap Syndromes in Autoimmune Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 32414025
- PMCID: PMC7291241
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm9051449
Treatment of Overlap Syndromes in Autoimmune Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
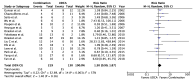
The treatment of overlap syndromes is guided by small observational studies whose data have never been synthesized in a rigorous, quantitative manner. We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate the efficacy of available treatments for these rare and morbid conditions. We searched the literature for studies comparing ≥2 therapies for autoimmune hepatitis (AIH)-primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), AIH-primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC), PBC-PSC, AIH-PBC-PSC, autoimmune cholangitis (AIC), or autoimmune sclerosing cholangitis (ASC) with respect to various clinical outcomes, including biochemical improvement and transplant-free survival. A total of 28 studies met the inclusion criteria for AIH-PBC, AIH-PSC, AIC, and ASC. AIH-PBC patients tended to experience more biochemical improvement with ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) + [corticosteroids and/or antimetabolites], i.e., "combination therapy", than with corticosteroids ± azathioprine (RR = 4.00, 95% CI 0.93-17.18). AIH-PBC patients had higher transplant-free survival with combination therapy than with UDCA, but only when studies with follow-up periods ≤90 months were excluded (RR = 6.50, 95% CI 1.47-28.83). Combination therapy may therefore be superior to both UDCA and corticosteroids ± azathioprine for the treatment of AIH-PBC, but additional studies are needed to show this definitively and to elucidate optimal treatments for other overlap syndromes.
Keywords: autoimmune liver disease; corticosteroid; immunosuppression; overlap syndrome; ursodeoxycholic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




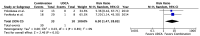

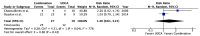

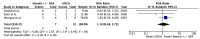



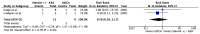
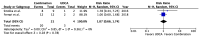


References
-
- Lohse A.W., Büschenfelde K.-H.M.Z., Franz B., Kanzler S., Gerken G., Dienes H.P. Characterization of the overlap syndrome of primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) and autoimmune hepatitis: Evidence for it being a hepatitic form of PBC in genetically susceptible individuals. Hepatology. 1999;29:1078–1084. doi: 10.1002/hep.510290409. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

