Can Teledentistry Improve the Monitoring of Patients during the Covid-19 Dissemination? A Descriptive Pilot Study
- PMID: 32414126
- PMCID: PMC7277372
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17103399
Can Teledentistry Improve the Monitoring of Patients during the Covid-19 Dissemination? A Descriptive Pilot Study
Abstract
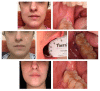
The aim of this pilot study was to describe the advantages of telemedicine (TM) in dental practice during the current national emergency condition due to the Covid-19 dissemination. At Department of Oral Surgery and Pathology-Magna Graecia University of Catanzaro, regional reference center for Covid-19-two groups of patients were determined: patients with urgent conditions (group U) and patients in follow-up (group F). Both groups were instructed to implement remote consultations using a messaging service (WhatsApp Messenger, WhatsApp Inc., Mountain View, California, USA) to send photos. A total of 418 photos were collected by 57 patients. Thirty-four photos were obtained by five patients in the U group after surgical procedures. All patients sent photos on the established evening, except for two patients who sent two photos outside the set days. In the F group, 384 photos were collected by 52 patients. None of them sent more photos than the number that was established by the protocol. Telemedicine allowed a monitoring of all patients, reducing costs and limiting human contact, decreasing the risk of Covid-19 dissemination.
Keywords: Covid-19; WhatsApp; community dentistry; dental public health; dentistry; teledentistry; telemedicine.
Conflict of interest statement
General practitioner
Figures

References
-
- Kwok K.O., Li K.K., Chan H.H., Yi Y.Y., Tang A., Wei W.I., Wong Y.S. Community responses during the early phase of the COVID-19 epidemic in Hong Kong: Risk perception, information exposure and preventive measures. medRxiv. 2020 doi: 10.1101/2020.02.26.20028217. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

