Impact evaluation of the free maternal healthcare policy on the risk of neonatal and infant deaths in four sub-Saharan African countries: a quasi-experimental design with propensity score Kernel matching and difference in differences analysis
- PMID: 32414818
- PMCID: PMC7232624
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-033356
Impact evaluation of the free maternal healthcare policy on the risk of neonatal and infant deaths in four sub-Saharan African countries: a quasi-experimental design with propensity score Kernel matching and difference in differences analysis
Abstract
Objective: Despite the huge financial investment in the free maternal healthcare policy (FMHCP) by the Governments of Ghana and Burkina Faso, no study has quantified the impact of FMHCP on the relative reduction in neonatal and infant mortality rates using a more rigorous matching procedure with the difference in differences (DID) analysis. This study used several rounds of publicly available population-based complex survey data to determine the impact of FMHCP on neonatal and infant mortality rates in these two countries.
Design: A quasi-experimental study to evaluate the FMHCP implemented in Burkina Faso and Ghana between 2007 and 2014.
Setting: Demographic and health surveys and maternal health surveys conducted between 2000 and 2014 in Ghana, Burkina Faso, Nigeria and Zambia.
Participants: Children born 5 years preceding the survey in Ghana, Burkina Faso, Nigeria and Zambia.
Primary outcome measures: Neonatal and infant mortality rates.
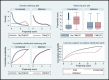
Results: The Propensity Score Kernel Matching coupled with DID analysis with modified Poisson showed that the FMHCP was associated with a 45% reduction in the risk of neonatal mortality rate in Ghana and Burkina Faso compared with Nigeria and Zambia (adjusted relative risk (aRR)=0.55, 95% CI: 0.40 to 0.76, p<0.001). In addition, infant mortality rate has reduced significantly in both Ghana and Burkina Faso by approximately 54% after full implementation of FMHCP compared with Nigeria and Zambia (aRR=0.46, 95% CI: 0.36 to 0.59, p<0.001).
Conclusion: The FMHCP had a significant impact and still remains relevant in achieving Sustainable Development Goal 3 and could provide lessons for other sub-Saharan countries in the design and implementation of a similar policy.
Keywords: free maternal healthcare policy; infant mortality; neonatal mortality; public health.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2020. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Wang H, Otoo N, Dsane-Selby L. Ghana National Health Insurance Scheme: improving financial sustainability based on expenditure review. The World Bank, 2017.
-
- Organization WH, UNICEF . Trends in maternal mortality: 1990-2015: estimates from who, UNICEF, UNFPA, world bank group and the United nations population division, 2015.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
