Characterization of lactic acid bacteria derived exopolysaccharides for use as a defined neuroprotective agent against amyloid beta1-42-induced apoptosis in SH-SY5Y cells
- PMID: 32415207
- PMCID: PMC7229009
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-65147-1
Characterization of lactic acid bacteria derived exopolysaccharides for use as a defined neuroprotective agent against amyloid beta1-42-induced apoptosis in SH-SY5Y cells
Abstract
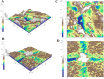
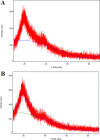
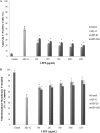
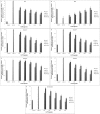
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a disease characterized by cerebral neuronal degeneration and loss in a progressive manner. Amyloid beta (Aβ) in the brain is toxic to neurons, being a main risk factor for initiation and continuation of cognitive deterioration in AD. Neurotoxicity of Aβ origin is also linked to oxidative stress characterized by excessive lipid peroxidation, protein oxidation, changes in antioxidant systems, and cerebral DNA damage in AD. Furthermore, Aβ can induce oxidative neuronal cell death by a mitochondrial dysfunction. Cellular injury caused by oxidative stress can be possibly prevented by boosting or promoting bodily oxidative defense system by supplying antioxidants in diet or as medications. However, most synthetic antioxidants are found to have cytotoxicity, which prevents their safe use, and limits their administration. For this reason, more attention has been paid to the natural non-toxic antioxidants. One of the most promising groups of non-toxic antioxidative compounds is thought to be polysaccharides. This study investigated the characterization and protective action exerted by exopolysaccharides (EPSs) originated from Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus B3 and Lactobacillus plantarum GD2 to protect from apoptotic activity exerted by Aβ1-42 among SH-SY5Y cells. We characterized EPSs by elemental analysis, FTIR, AFM, SEM, and XRD. The antioxidant effects of EPSs were determined by the DPPH free radical scavenging activity, hydroxyl radical scavenging activity, metal ion chelating activity, lipid peroxidation inhibitory activity, and superoxide anion scavenging activity method. The protective effects of EPSs were determined by flow cytometry and RT-PCR. Mannose ratio, molecular weight, functional groups, surface morphology, and amorphous character structure of EPSs are thought to play a role in the protective effect of EPSs. EPSs reduced apoptotic activity of Aβ1-42 in addition to their depolarizing effect on mitochondrial membrane potential in concentration-dependent manner. These observations contribute the inclusion of EPSs among the therapeutic options used to manage various neurological disorders in the traditional medicine in a scientific manner, indicating that EPSs may be promising natural chemical constituents that need advanced research and development for pharmacological therapy of AD.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Phytochemical Ginkgolide B Attenuates Amyloid-β1-42 Induced Oxidative Damage and Altered Cellular Responses in Human Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y Cells.J Alzheimers Dis. 2017;60(s1):S25-S40. doi: 10.3233/JAD-161086. J Alzheimers Dis. 2017. PMID: 28234255
-
N-Feruloyl Serotonin Attenuates Neuronal Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in Aβ25-35-Treated Human Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y Cells.Molecules. 2023 Feb 7;28(4):1610. doi: 10.3390/molecules28041610. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36838597 Free PMC article.
-
Dose-dependent folic acid and memantine treatments promote synergistic or additive protection against Aβ(25-35) peptide-induced apoptosis in SH-SY5Y cells mediated by mitochondria stress-associated death signals.Food Chem Toxicol. 2013 Dec;62:538-47. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2013.09.015. Epub 2013 Sep 17. Food Chem Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 24055771
-
Antioxidant potential of exopolysaccharides from lactic acid bacteria: A comprehensive review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Nov;281(Pt 2):135536. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.135536. Epub 2024 Sep 30. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 39349319 Review.
-
Vitamin E as an antioxidant/free radical scavenger against amyloid beta-peptide-induced oxidative stress in neocortical synaptosomal membranes and hippocampal neurons in culture: insights into Alzheimer's disease.Rev Neurosci. 1999;10(2):141-9. doi: 10.1515/revneuro.1999.10.2.141. Rev Neurosci. 1999. PMID: 10658956 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Characterization and Biocompatibility of Exopolysaccharide Produced by Moderately Halophilic Bacterium Virgibacillus dokdonensis from the Saltern of Kumta Coast.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Sep 23;14(19):3986. doi: 10.3390/polym14193986. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36235941 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Lab4P Probiotic Effects on Cognition in 3xTg-AD Alzheimer's Disease Model Mice and the SH-SY5Y Neuronal Cell Line.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 28;24(5):4683. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054683. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36902113 Free PMC article.
-
Purification, Structural Characteristics, and Biological Activities of Exopolysaccharide Isolated From Leuconostoc mesenteroides SN-8.Front Microbiol. 2021 Mar 26;12:644226. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.644226. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33841368 Free PMC article.
-
Gut microbiota in ischemic stroke: Where we stand and challenges ahead.Front Nutr. 2022 Dec 1;9:1008514. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1008514. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36532541 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Cross-sectional In Vitro Study on the Synergistic Neuroprotective Effects of Phytochemicals Ferulic Acid and Ginkgolide B against Amyloid Beta-induced Oxidative Stress and Modulation of Multifunctional Enzyme APE1/Ref-1 in Human Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y Cells.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025 Jun 16. doi: 10.1007/s12013-025-01799-y. Online ahead of print. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025. PMID: 40522419
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

