High circulating levels of midregional proenkephalin A predict vascular dementia: a population-based prospective study
- PMID: 32415209
- PMCID: PMC7229155
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-64998-y
High circulating levels of midregional proenkephalin A predict vascular dementia: a population-based prospective study
Abstract
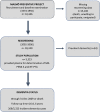
Midregional Pro-enkephalin A (MR-PENK A) and N-terminal Protachykinin A (NT-PTA) have been associated with vascular dementia. However, the longitudinal relationship between these biomarkers and incident dementia has not been fully investigated. In the population-based Malmö Preventive Project, circulating levels of MR-PENK A and NT-PTA were determined in a random sample of 5,323 study participants (mean age: 69 ± 6 years) who were followed-up over a period of 4.6 ± 1.6 years. The study sample included 369 patients (7%) who were diagnosed in the same period with dementia. We analyzed relationship of MR-PENK A and NT-PTA with the risk of developing dementia by using multivariable-adjusted Cox regression models adjusted for traditional risk factors. Increased plasma levels of MR-PENK A were associated with higher risk of incident vascular dementia whereas no associations were found with all-cause or Alzheimer dementia. The risk of vascular dementia was mainly conferred by the highest quartile of MR-PENK as compared with lower quartiles. Elevated levels of NT-PTA yielded significant association with all-cause dementia or dementia subtypes. Elevated plasma concentration of MR-PENK A independently predicts vascular dementia in the general population. MR-PENK A may be used as an additional tool for identifying vascular subtype in ambiguous dementia cases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
N-Terminal Prosomatostatin and Risk of Vascular Dementia.Cerebrovasc Dis. 2017;44(5-6):259-265. doi: 10.1159/000479940. Epub 2017 Aug 31. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2017. PMID: 28854435
-
Midregional Proenkephalin A and N-terminal Protachykinin A are decreased in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with dementia disorders and acute neuroinflammation.J Neuroimmunol. 2010 Apr 15;221(1-2):62-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2010.02.004. Epub 2010 Mar 5. J Neuroimmunol. 2010. PMID: 20207019
-
Elevated plasma levels of neuropeptide proenkephalin a predict mortality and functional outcome in ischemic stroke.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012 Jul 24;60(4):346-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2012.04.024. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012. PMID: 22813614
-
Proenkephalin: A New Biomarker for Glomerular Filtration Rate and Acute Kidney Injury.Nephron. 2020;144(12):655-661. doi: 10.1159/000509352. Epub 2020 Jul 31. Nephron. 2020. PMID: 32739920 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hyperhomocysteinemia and risk of incident cognitive outcomes: An updated dose-response meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies.Ageing Res Rev. 2019 May;51:55-66. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2019.02.006. Epub 2019 Feb 28. Ageing Res Rev. 2019. PMID: 30826501 Review.
Cited by
-
Plasma Pro-Enkephalin A and Incident Cognitive Impairment: The Reasons for Geographic and Racial Differences in Stroke Cohort.J Am Heart Assoc. 2023 Jun 6;12(11):e029081. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.122.029081. Epub 2023 Jun 1. J Am Heart Assoc. 2023. PMID: 37260023 Free PMC article.
-
Blood biomarkers for vascular cognitive impairment based on neuronal function: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Neurol. 2025 Feb 7;16:1496711. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1496711. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 39990267 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasma Pro-Enkephalin A and Ischemic Stroke Risk: The Reasons for Geographic and Racial Differences in Stroke Cohort.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2022 Feb;31(2):106237. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2021.106237. Epub 2021 Dec 9. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2022. PMID: 34896817 Free PMC article.
-
Pro-Enkephalin and its association with renal function in Middle Eastern immigrants and native Swedes.Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2021 Nov;81(7):573-578. doi: 10.1080/00365513.2021.1979243. Epub 2021 Sep 28. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2021. PMID: 34581639 Free PMC article.
-
Paracrine Interleukin 6 Induces Cerebral Remodeling at Early Stages After Unilateral Common Carotid Artery Occlusion in Mice.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Jan 27;8:805095. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.805095. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35155612 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Prince, M. World Alzheimer Report 2016 (2016).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

