Woody Plant Encroachment has a Larger Impact than Climate Change on Dryland Water Budgets
- PMID: 32415221
- PMCID: PMC7229153
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-65094-x
Woody Plant Encroachment has a Larger Impact than Climate Change on Dryland Water Budgets
Abstract
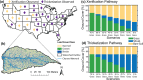
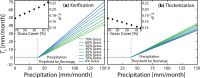
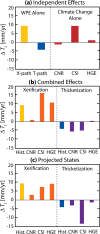
Woody plant encroachment (WPE) into grasslands is a global phenomenon that is associated with land degradation via xerification, which replaces grasses with shrubs and bare soil patches. It remains uncertain how the global processes of WPE and climate change may combine to impact water availability for ecosystems. Using a process-based model constrained by watershed observations, our results suggest that both xerification and climate change augment groundwater recharge by increasing channel transmission losses at the expense of plant available water. Conversion from grasslands to shrublands without creating additional bare soil, however, reduces transmission losses. Model simulations considering both WPE and climate change are used to assess their relative roles in a late 21st century condition. Results indicate that changes in focused channel recharge are determined primarily by the WPE pathway. As a result, WPE should be given consideration when assessing the vulnerability of groundwater aquifers to climate change.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Asner GP, et al. Grazing systems, ecosystem responses and global change. Annual Reviews of Environmental Resources. 2004;29:261–299. doi: 10.1146/annurev.energy.29.062403.102142. - DOI
-
- Wilcox BP. Transformative ecosystem change and ecohydrology: Ushering in a new era for watershed management. Ecohydrology. 2010;3:120–130.
-
- Van Auken OW. Shrub invasions of North American semiarid grasslands. Annual Reviews of Ecological Systems. 2000;31:197–215. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.31.1.197. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

