Coronavirus disease 2019 in renal transplant recipients: Report of two cases
- PMID: 32415905
- PMCID: PMC7267089
- DOI: 10.1111/tid.13329
Coronavirus disease 2019 in renal transplant recipients: Report of two cases
Abstract
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has been a pandemic worldwide. The data about COVID-19 in renal transplant recipient are deficiency. Herein, we report two COVID-19 cases in renal transplant recipients. Both cases were discharged following a treatment regimen including discontinued immunosuppressant and low-dose methylprednisolone-based therapy. There were no signs of rejection during the treatment. These successfully treated cases can provide helpful information about the management of COVID-19 in renal transplant recipients.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; immunosuppressant; methylprednisolone; renal transplant recipient.
© 2020 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Figures
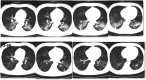
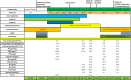
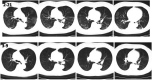
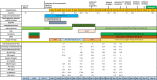
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

