Synthetic Lethal and Resistance Interactions with BET Bromodomain Inhibitors in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- PMID: 32416067
- PMCID: PMC7306005
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2020.04.027
Synthetic Lethal and Resistance Interactions with BET Bromodomain Inhibitors in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Abstract
BET bromodomain inhibitors (BBDIs) are candidate therapeutic agents for triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) and other cancer types, but inherent and acquired resistance to BBDIs limits their potential clinical use. Using CRISPR and small-molecule inhibitor screens combined with comprehensive molecular profiling of BBDI response and resistance, we identified synthetic lethal interactions with BBDIs and genes that, when deleted, confer resistance. We observed synergy with regulators of cell cycle progression, YAP, AXL, and SRC signaling, and chemotherapeutic agents. We also uncovered functional similarities and differences among BRD2, BRD4, and BRD7. Although deletion of BRD2 enhances sensitivity to BBDIs, BRD7 loss leads to gain of TEAD-YAP chromatin binding and luminal features associated with BBDI resistance. Single-cell RNA-seq, ATAC-seq, and cellular barcoding analysis of BBDI responses in sensitive and resistant cell lines highlight significant heterogeneity among samples and demonstrate that BBDI resistance can be pre-existing or acquired.
Keywords: ATAC-seq; BET bromodomain inhibitors; CRISPR screen; ChIP-seq; cellular barcoding; single cell ATAC-seq; single cell RNA-seq; small molecule inhibitor screen; therapeutic resistance; triple-negative breast cancer.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests M.B. and K.P. received research support and were consultants to the Novartis Institutes for BioMedical Research during the execution of this study. K.P. serves on the scientific advisory board of Farcast Biosciences and Acrivon Therapeutics. M.B. receives sponsored research support from Novartis, serves on the SAB of Kronos Bio, and is a consultant to GTx, Inc., Aleta Biotherapeutics, and H3 Biomedicine. R.Z. and J.B. are current employees of C4 Therapeutics Inc. and Novartis, respectively. C.K. is a scientific founder, fiduciary board of directors member, scientific advisory board member, consultant, and shareholder of Foghorn Therapeutics, Inc. (Cambridge, MA). S. Shu, K.P., and J.B. are inventors of a patent on BET inhibitor resistance that DFCI licensed to Roche.
Figures


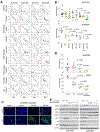
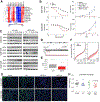



Comment in
-
Place Your BETs in Combination Therapy.Mol Cell. 2020 Jun 18;78(6):991-993. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2020.05.026. Mol Cell. 2020. PMID: 32559426
References
-
- Abraham J, Coleman R, Elias A, Holmes FA, Kalinsky K, Kittaneh M, Lower E, Mahtani R, Terry Mamounas E, Pegram M, et al. (2018). Use of cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 4/6 inhibitors for hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative, metastatic breast cancer: a roundtable discussion by The Breast Cancer Therapy Expert Group (BCTEG). Breast Cancer Res Treat 171, 11–20. - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y, and Hochberg Y (1995). Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing J. Royal Statistical Society 57, 289–300.
-
- Bhang HE, Ruddy DA, Krishnamurthy Radhakrishna V, Caushi JX, Zhao R, Hims MM, Singh AP, Kao I, Rakiec D, Shaw P, et al. (2015). Studying clonal dynamics in response to cancer therapy using high-complexity barcoding. Nat Med 21, 440–448. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

