Changes in Children's Healthcare Visits During Coronavirus Disease-2019 Pandemic in Hangzhou, China
- PMID: 32416087
- PMCID: PMC7235594
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2020.05.013
Changes in Children's Healthcare Visits During Coronavirus Disease-2019 Pandemic in Hangzhou, China
Abstract
The lower than expected rates of children affected by coronavirus disease-2019 does not mean that there was no impact on children's health. Using data on pediatric healthcare visits before and after the breakout of coronavirus disease-2019 and historical data, we identified pediatric conditions that were most affected by the pandemic and epidemic control measures during the pandemic.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
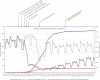
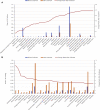
Comment in
-
Changes in hospitalization in children during COVID-19 pandemic quarantine in a single center in Turkey.J Pediatr. 2021 Apr;231:296-297. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2020.12.014. Epub 2020 Dec 15. J Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 33333113 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Reply.J Pediatr. 2021 Apr;231:297-298. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2020.12.015. Epub 2020 Dec 17. J Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 33346047 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) WHO; Geneva: 2020. Coronavirus disease (COVID-2019) situation reports.
-
- Wu Z., McGoogan J.M. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China. JAMA. 2020;323:1239–1242. - PubMed
-
- Castagnoli R., Votto M., Licari A., Brambilla I., Bruno R., Perlini S. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection in children and adolescents: a systematic review. JAMA Pediatr. 2020 [Epub ahead of print] - PubMed
-
- Cruz A.T., Zeichner S.L. COVID-19 in children: initial characterization of the pediatric disease. Pediatrics. 2020:e20200834. - PubMed
-
- Golberstein E., Wen H., Miller B.F. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and mental health for children and adolescents. JAMA Pediatr. 2020 [Epub ahead of print] - PubMed

