Orally ingestible medical devices for gut engineering
- PMID: 32416112
- PMCID: PMC7255201
- DOI: 10.1016/j.addr.2020.05.004
Orally ingestible medical devices for gut engineering
Abstract
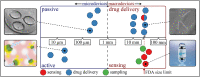
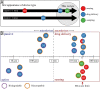
Orally ingestible medical devices provide significant advancement for diagnosis and treatment of gastrointestinal (GI) tract-related conditions. From micro- to macroscale devices, with designs ranging from very simple to complex, these medical devices can be used for site-directed drug delivery in the GI tract, real-time imaging and sensing of gut biomarkers. Equipped with uni-direction release, or self-propulsion, or origami design, these microdevices are breaking the barriers associated with drug delivery, including biologics, across the GI tract. Further, on-board microelectronics allow imaging and sensing of gut tissue and biomarkers, providing a more comprehensive understanding of underlying pathophysiological conditions. We provide an overview of recent advances in orally ingestible medical devices towards drug delivery, imaging and sensing. Challenges associated with gut microenvironment, together with various activation/actuation modalities of medical devices for micromanipulation of the gut are discussed. We have critically examined the relationship between materials-device design-pharmacological responses with respect to existing regulatory guidelines and provided a clear roadmap for the future.
Keywords: GI diagnostics; Gastrointestinal tract; Gut microbiota; Medical microdevices; Oral drug delivery.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Otsuka F., Vorpahl M., Nakano M., Foerst J., Newell J.B., Sakakura K., Kutys R., Ladich E., Finn A.V., Kolodgie F.D. Pathology of second-generation Everolimus-eluting stents versus first-generation Sirolimus-and paclitaxel-eluting stents in humans. Circulation. 2014 doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.001790. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

