The SecA ATPase motor protein binds to Escherichia coli liposomes only as monomers
- PMID: 32416191
- PMCID: PMC7316483
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2020.183358
The SecA ATPase motor protein binds to Escherichia coli liposomes only as monomers
Abstract
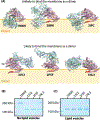
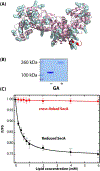
The essential SecA motor ATPase acts in concert with the SecYEG translocon to secrete proteins into the periplasmic space of Escherichia coli. In aqueous solutions, SecA exists largely as dimers, but the oligomeric state on membranes is less certain. Crystallographic studies have suggested several possible solution dimeric states, but its oligomeric state when bound to membranes directly or indirectly via the translocon is controversial. We have shown using disulfide crosslinking that the principal solution dimer, corresponding to a crystallographic dimer (PDB 1M6N), binds only weakly to large unilamellar vesicles (LUV) formed from E. coli lipids. We report here that other soluble crosslinked crystallographic dimers also bind weakly, if at all, to LUV. Furthermore, using a simple glutaraldehyde crosslinking scheme, we show that SecA is always monomeric when bound to LUV formed from E. coli lipids.
Keywords: Disulfide crosslinking; Glutaraldehyde crosslinking; Large unilamellar vesicles (LUV); Protein partitioning; Protein secretion.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Topology of the SecA ATPase Bound to Large Unilamellar Vesicles.J Mol Biol. 2022 Jun 30;434(12):167607. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2022.167607. Epub 2022 Apr 27. J Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35489383 Free PMC article.
-
Binding of SecA ATPase monomers and dimers to lipid vesicles.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2020 Feb 1;1862(2):183112. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2019.183112. Epub 2019 Oct 30. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2020. PMID: 31676370 Free PMC article.
-
The oligomeric state and arrangement of the active bacterial translocon.J Biol Chem. 2011 Feb 11;286(6):4659-69. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.175638. Epub 2010 Nov 5. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21056980 Free PMC article.
-
SecA - a multidomain and multitask bacterial export protein.Acta Biochim Pol. 2021 Aug 31;68(3):427-436. doi: 10.18388/abp.2020_5761. Acta Biochim Pol. 2021. PMID: 34463460 Review.
-
Protein Transport Across the Bacterial Plasma Membrane by the Sec Pathway.Protein J. 2019 Jun;38(3):262-273. doi: 10.1007/s10930-019-09841-8. Protein J. 2019. PMID: 31134461 Review.
Cited by
-
Probing macromolecular crowding at the lipid membrane interface with genetically-encoded sensors.Protein Sci. 2023 Nov;32(11):e4797. doi: 10.1002/pro.4797. Protein Sci. 2023. PMID: 37779215 Free PMC article.
-
A unifying mechanism for protein transport through the core bacterial Sec machinery.Open Biol. 2023 Aug;13(8):230166. doi: 10.1098/rsob.230166. Epub 2023 Aug 30. Open Biol. 2023. PMID: 37643640 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Towards a Quantitative Understanding of Protein-Lipid Bilayer Interactions at the Single Molecule Level: Opportunities and Challenges.J Membr Biol. 2021 Feb;254(1):17-28. doi: 10.1007/s00232-020-00151-0. Epub 2020 Nov 16. J Membr Biol. 2021. PMID: 33196888 Review.
-
Topology of the SecA ATPase Bound to Large Unilamellar Vesicles.J Mol Biol. 2022 Jun 30;434(12):167607. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2022.167607. Epub 2022 Apr 27. J Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35489383 Free PMC article.
-
The Dynamic SecYEG Translocon.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Apr 15;8:664241. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.664241. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33937339 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cabelli RJ, Dolan KM, Qian L, Oliver DB, Characterization of membrane-associated and soluble states of SecA protein from wild-type and SecA51(TS) mutant strains of Escherichia coli, J. Biol. Chem, 266 (1991) 24420–24427. - PubMed
-
- de Vrije T, de Swart RL, Dowhan W, Tommassen J, de Kruijff B, Phosphatidylglycerol is involved in protein translocation across Escherichia coli inner membranes, Nature, 334 (1988) 173–175. - PubMed
-
- Prabudiansyah I, Kusters I, Caforio A, Driessen AJM, Characterization of the annular lipid shell of the Sec translocon, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1848 (2015) 2050–2056. - PubMed
-
- Breukink E, Demel RA, de Korte-Kool G, de Kruijff B, SecA insertion into phospholipids is stimulated by negatively charged lipids and inhibited by ATP: a monolayer study, Biochemistry, 31 (1992) 1119–1124. - PubMed

