Comparison of seven commercial RT-PCR diagnostic kits for COVID-19
- PMID: 32416600
- PMCID: PMC7206434
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104412
Comparison of seven commercial RT-PCR diagnostic kits for COVID-19
Abstract
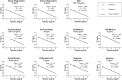
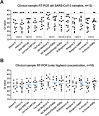
The final months of 2019 witnessed the emergence of a novel coronavirus in the human population. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has since spread across the globe and is posing a major burden on society. Measures taken to reduce its spread critically depend on timely and accurate identification of virus-infected individuals by the most sensitive and specific method available, i.e. real-time reverse transcriptase PCR (RT-PCR). Many commercial kits have recently become available, but their performance has not yet been independently assessed. The aim of this study was to compare basic analytical and clinical performance of selected RT-PCR kits from seven different manufacturers (Altona Diagnostics, BGI, CerTest Biotec, KH Medical, PrimerDesign, R-Biopharm AG, and Seegene). We used serial dilutions of viral RNA to establish PCR efficiency and estimate the 95 % limit of detection (LOD95). Furthermore, we ran a panel of SARS-CoV-2-positive clinical samples (n = 13) for a preliminary evaluation of clinical sensitivity. Finally, we used clinical samples positive for non-coronavirus respiratory viral infections (n = 6) and a panel of RNA from related human coronaviruses to evaluate assay specificity. PCR efficiency was ≥96 % for all assays and the estimated LOD95 varied within a 6-fold range. Using clinical samples, we observed some variations in detection rate between kits. Importantly, none of the assays showed cross-reactivity with other respiratory (corona)viruses, except as expected for the SARS-CoV-1 E-gene. We conclude that all RT-PCR kits assessed in this study may be used for routine diagnostics of COVID-19 in patients by experienced molecular diagnostic laboratories.
Keywords: COVID-19; Coronavirus; In vitro diagnostics; RT-PCR; SARS-CoV-2; nCoV-2019.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest None.
Figures
Comment in
-
Letter of concern re: "Comparison of seven commercial RT-PCR diagnostic kits for COVID-19" van Kasteren et al., Journal of Clinical Virology.J Clin Virol. 2020 Sep;130:104536. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104536. Epub 2020 Jul 6. J Clin Virol. 2020. PMID: 32745967 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Comment on
-
Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR.Euro Surveill. 2020 Jan;25(3):2000045. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.3.2000045. Euro Surveill. 2020. PMID: 31992387 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

