Early exit from neonatal therapeutic hypothermia: A single institution experience using MRI to guide decision-making
- PMID: 32417801
- PMCID: PMC8477306
- DOI: 10.3233/NPM-200458
Early exit from neonatal therapeutic hypothermia: A single institution experience using MRI to guide decision-making
Abstract
Background: To evaluate the feasibility of a protocol using combined magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), clinical data, and electroencephalogram (EEG) to identify neonates with mild neonatal encephalopathy (NE) treated with therapeutic hypothermia (TH) who are eligible for "early exit".
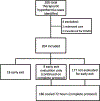
Methods: Retrospective chart review of TH cases at a single Level III NICU over a 5-year period was used to describe the demographic, clinical, and outcome data in neonates that received early exit in contrast to 72 hour TH treatment.
Results: Two hundred and eight TH cases, including 18 early exit cases (9%) and 9 cases (4%) evaluated for early exit with MRI but continued on 72 hours of TH, were identified. Early exit and 72 hour treatment groups did not differ in demographics or cord gas measures, although early exit neonates had a shorter length of stay (p < 0.05). Consistent with the early exit protocol, no early exit infants had evidence of moderate or severe encephalopathy on EEG or evidence of hypoxic ischemic injury on MRI at 24 hours of life. Neurology follow up between age 1 and 18 months was available for 10 early exit infants, 8 of whom had a normal examination.
Conclusions: Early MRI at 24 hours of age, alongside clinical and EEG criteria, is feasible as part of a protocol to identify neonates eligible for early exit from therapeutic hypothermia.
Keywords: Neonatal encephalopathy; early exit; hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy; therapeutic hypothermia.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure statements
Drs. White, Grant, Soul, Inder, and El-Dib have no conflicts of interest or financial disclosures.
References
-
- Committee on Fetus and Newborn, Papile LA, Baley JE, Benitz W, Cummings J, et al. Hypothermia and neonatal encephalopathy. Pediatrics. 2014;133(6):1146–50. - PubMed
-
- Gluckman PD, Wyatt JS, Azzopardi D, Ballard R, Edwards AD, Ferriero DM, et al. Selective head cooling with mild systemic hypothermia after neonatal encephalopathy: multicentre randomised trial. Lancet. 2005;365(9460):663–70. - PubMed
-
- Shankaran S, Laptook AR, Ehrenkranz RA, Tyson JE, McDonald SA, Donovan EF, et al. Whole-body hypothermia for neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(15):1574–84. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical