Epidemiology of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Caused by Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)
- PMID: 32418549
- PMCID: PMC7399147
- DOI: 10.1017/dmp.2020.155
Epidemiology of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Caused by Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)
Abstract
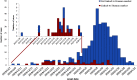
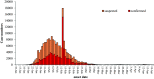
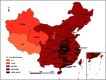
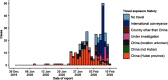
In December, 2019, an infectious outbreak of unknown cause occurred in Wuhan, which attracted intense attention. Shortly after the virus was identified as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the epidemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) broke out, and an information storm occurred. At that time, 2 important aspects, that is, the stages of spread and the components of the epidemic, were unclear. Answers to the questions (1) what are the sources, (2) how do infections occur, and (3) who will be affected should be clarified as the outbreak continues to evolve. Furthermore, components of the epidemic and the stages of spread should be explored and discussed. Based on information of SARS, Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS), and COVID-19, the components of the epidemic (the sources, the routes of infection, and the susceptible population) will be discussed, as well as the role of natural and social factors involved. Epidemiologic characteristics of patients will be traced based on current information.
Keywords: coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19); epidemic SARS-CoV-2; epidemiology characteristics; epidemiology process; links.
Figures
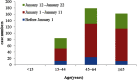
References
-
- The National Health Commission (NHC). Daily announcements of epidemic situation of China (April 18, 2020). NHC website. http://www.nhc.gov.cn/xcs/yqtb/202004/2d391a171acc4624a50a1188c8de7361.s.... Accessed May 6, 2020.
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) situation report – 89 (April 18, 2020). WHO website. https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/2.... Accessed May 6, 2020.
-
- The National Health Commission (NHC). Daily announcements of epidemic situation of China (January 24, 2020). NHC website. http://www.nhc.gov.cn/xcs/yqtb/202001/c5da49c4c5bf4bcfb320ec2036480627.s.... Accessed May 6, 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

