MEF2C Hypofunction in Neuronal and Neuroimmune Populations Produces MEF2C Haploinsufficiency Syndrome-like Behaviors in Mice
- PMID: 32418612
- PMCID: PMC7483399
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2020.03.011
MEF2C Hypofunction in Neuronal and Neuroimmune Populations Produces MEF2C Haploinsufficiency Syndrome-like Behaviors in Mice
Erratum in
-
Erratum.Biol Psychiatry. 2023 May 1;93(9):852. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2023.02.011. Biol Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37045513 No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Microdeletions of the MEF2C gene are linked to a syndromic form of autism termed MEF2C haploinsufficiency syndrome (MCHS). MEF2C hypofunction in neurons is presumed to underlie most of the symptoms of MCHS. However, it is unclear in which cell populations MEF2C functions to regulate neurotypical development.
Methods: Multiple biochemical, molecular, electrophysiological, behavioral, and transgenic mouse approaches were used to characterize MCHS-relevant synaptic, behavioral, and gene expression changes in mouse models of MCHS.
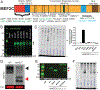
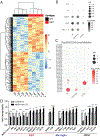
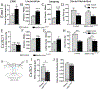
Results: We showed that MCHS-associated missense mutations cluster in the conserved DNA binding domain and disrupt MEF2C DNA binding. DNA binding-deficient global Mef2c heterozygous mice (Mef2c-Het) displayed numerous MCHS-related behaviors, including autism-related behaviors, changes in cortical gene expression, and deficits in cortical excitatory synaptic transmission. We detected hundreds of dysregulated genes in Mef2c-Het cortex, including significant enrichments of autism risk and excitatory neuron genes. In addition, we observed an enrichment of upregulated microglial genes, but this was not due to neuroinflammation in the Mef2c-Het cortex. Importantly, conditional Mef2c heterozygosity in forebrain excitatory neurons reproduced a subset of the Mef2c-Het phenotypes, while conditional Mef2c heterozygosity in microglia reproduced social deficits and repetitive behavior.
Conclusions: Taken together, our findings show that mutations found in individuals with MCHS disrupt the DNA-binding function of MEF2C, and DNA binding-deficient Mef2c global heterozygous mice display numerous MCHS-related phenotypes, including excitatory neuron and microglia gene expression changes. Our findings suggest that MEF2C regulates typical brain development and function through multiple cell types, including excitatory neuronal and neuroimmune populations.
Keywords: Autism; Mef2c; Microglia; Mouse; Neurodevelopmental disorder; Neuron.
Copyright © 2020 Society of Biological Psychiatry. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures:
All authors report no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
MEF2C Hypofunction in GABAergic Cells Alters Sociability and Prefrontal Cortex Inhibitory Synaptic Transmission in a Sex-Dependent Manner.Biol Psychiatry Glob Open Sci. 2024 Jan 16;4(2):100289. doi: 10.1016/j.bpsgos.2024.100289. eCollection 2024 Mar. Biol Psychiatry Glob Open Sci. 2024. PMID: 38390348 Free PMC article.
-
NitroSynapsin therapy for a mouse MEF2C haploinsufficiency model of human autism.Nat Commun. 2017 Nov 14;8(1):1488. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-01563-8. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 29133852 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral Auditory Nerve Impairment in a Mouse Model of Syndromic Autism.J Neurosci. 2022 Oct 19;42(42):8002-8018. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0253-22.2022. Epub 2022 Sep 30. J Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36180228 Free PMC article.
-
MEF2C haploinsufficiency syndrome: Report of a new MEF2C mutation and review.Eur J Med Genet. 2016 Sep;59(9):478-82. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2016.05.017. Epub 2016 May 31. Eur J Med Genet. 2016. PMID: 27255693 Review.
-
The function of Mef2c toward the development of excitatory and inhibitory cortical neurons.Front Cell Neurosci. 2024 Sep 23;18:1465821. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2024.1465821. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39376213 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular profiling of the hippocampus of children with autism spectrum disorder.Mol Psychiatry. 2024 Jul;29(7):1968-1979. doi: 10.1038/s41380-024-02441-8. Epub 2024 Feb 14. Mol Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38355786 Free PMC article.
-
Profiling Microglia in a Mouse Model of Machado-Joseph Disease.Biomedicines. 2022 Jan 23;10(2):237. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10020237. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35203447 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of miRNA expression and excitation in MEF2C autism patient hiPSC-neurons and cerebral organoids.Mol Psychiatry. 2025 Apr;30(4):1479-1496. doi: 10.1038/s41380-024-02761-9. Epub 2024 Sep 30. Mol Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 39349966 Free PMC article.
-
An epigenomic shift in amygdala marks the transition to maternal behaviors in alloparenting virgin female mice.PLoS One. 2022 Feb 22;17(2):e0263632. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0263632. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35192674 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a novel mutation in MEF2C gene in an atypical patient with frontotemporal lobar degeneration.Neurol Sci. 2022 Jan;43(1):319-326. doi: 10.1007/s10072-021-05269-0. Epub 2021 May 17. Neurol Sci. 2022. PMID: 33999292
References
-
- Flavell SW, Cowan CW, Kim TK, Greer PL, Lin Y, Paradis S, et al. (2006): Activity-dependent regulation of MEF2 transcription factors suppresses excitatory synapse number. Science. 311:1008–1012. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

