KSHV infection skews macrophage polarisation towards M2-like/TAM and activates Ire1 α-XBP1 axis up-regulating pro-tumorigenic cytokine release and PD-L1 expression
- PMID: 32418990
- PMCID: PMC7374093
- DOI: 10.1038/s41416-020-0872-0
KSHV infection skews macrophage polarisation towards M2-like/TAM and activates Ire1 α-XBP1 axis up-regulating pro-tumorigenic cytokine release and PD-L1 expression
Abstract
Background: Kaposi's Sarcoma Herpesvirus (KSHV) is a gammaherpesvirus strongly linked to human cancer. The virus is also able to induce immune suppression, effect that contributes to onset/progression of the viral-associated malignancies. As KSHV may infect macrophages and these cells abundantly infiltrate Kaposi's sarcoma lesions, in this study we investigated whether KSHV-infection could affect macrophage polarisation to promote tumorigenesis.
Methods: FACS analysis was used to detect macrophage markers and PD-L1 expression. KSHV infection and the molecular pathways activated were investigated by western blot analysis and by qRT-PCR while cytokine release was assessed by Multi-analyte Kit.
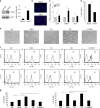
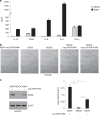
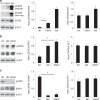
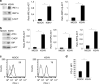
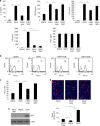
Results: We found that KSHV infection reduced macrophage survival and skewed their polarisation towards M2 like/TAM cells, based on the expression of CD163, on the activation of STAT3 and STAT6 pathways and the release of pro-tumorigenic cytokines such as IL-10, VEGF, IL-6 and IL-8. We also found that KSHV triggered Ire1 α-XBP1 axis activation in infected macrophages to increase the release of pro-tumorigenic cytokines and to up-regulate PD-L1 surface expression.
Conclusions: The findings that KSHV infection of macrophages skews their polarisation towards M2/TAM and that activate Ire1 α-XBP1 to increase the release of pro-tumorigenic cytokines and the expression of PD-L1, suggest that manipulation of UPR could be exploited to prevent or improve the treatment of KSHV-associated malignancies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Cirone M, Lucania G, Bergamo P, Trivedi P, Frati L, Faggioni A. Human herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8) inhibits monocyte differentiation into dendritic cells and impairs their immunostimulatory activity. Immunol. Lett. 2007;113:40–46. - PubMed
-
- Gilardini Montani MS, Falcinelli L, Santarelli R, Romeo MA, Granato M, Faggioni A, et al. Kaposi Sarcoma Herpes Virus (KSHV) infection inhibits macrophage formation and survival by counteracting Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor (M-CSF)-induced increase of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS), c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) phosphorylation and autophagy. Int J. Biochem Cell Biol. 2019;114:105560. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

