Novel potential tumor biomarkers: Circular RNAs and exosomal circular RNAs in gastrointestinal malignancies
- PMID: 32419229
- PMCID: PMC7370736
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.23359
Novel potential tumor biomarkers: Circular RNAs and exosomal circular RNAs in gastrointestinal malignancies
Abstract
Background: Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are structural ubiquitous RNA molecules. Accumulating evidences have elucidated that circRNAs play essential roles in the pathogenesis of diseases including cancers. Exosomal circRNAs are those circRNAs stably existing in exosomes and having high clinical values as novel potential diagnostic biomarkers of many diseases. Gastrointestinal (GI) malignancies, including pancreatic cancer, colorectal cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and gastric cancer, are leading causes of mortality worldwide and a major global health burden. However, no ideal tumor biomarkers of screening early GI cancers are currently available.
Methods: We collected data through Web of Science. The search terms used were as follows: circular RNA, circRNA, exosomes, exosomal circRNAs, biomarkers, gastrointestinal malignancies, pancreatic cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, HCC, gastric cancer, colorectal cancer, physiological functions, biogenesis, molecular mechanism. Only articles published in English were included.
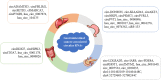
Results: We found that several circRNAs and exosomal circRNAs have been used as potential biomarkers to screen GI cancers including pancreatic cancer (hsa_circ_0001649, circ_0007534, circ_0030235, circRHOT1, circZMYM2, circ-LDLRAD3, chr14:101402109-101464448C, chr4:52729603-52780244C, circ-IARS, and circ-PDE8A), HCC (circSETD3, circADAMTS13, hsa_circ_0007874, hsa_circ_104135, circFBLIM1, cSMARCA5, circRNA-100338, and circPTGR1), colorectal cancer (hsa_circ_0001178, hsa_circ_0000826, hsa_circ_0004771, circDDX17, circITGA7, and circHIPK3), and gastric cancer (hsa_circ_0074362, circNRIP1, circAKT3, circ-DONSON, circPSMC3, circ-KIAA1244, circPVRL3, circPVT1, hsa_circ_0000096, ciRS-133, hsa_circ_0001017, and hsa_circ_0061276).
Conclusion: CircRNAs and exosomal circRNAs have the potential high clinical diagnostic values for GI malignancies.
Keywords: biomarkers; circular RNAs; exosome; gastrointestinal malignancies; non-invasive diagnosis.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tumor-suppressive circular RNAs: Mechanisms underlying their suppression of tumor occurrence and use as therapeutic targets.Cancer Sci. 2019 Dec;110(12):3630-3638. doi: 10.1111/cas.14211. Epub 2019 Oct 25. Cancer Sci. 2019. PMID: 31599076 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The diagnostic value of plasma exosomal hsa_circ_0070396 for hepatocellular carcinoma.Biomark Med. 2021 Apr;15(5):359-371. doi: 10.2217/bmm-2020-0476. Epub 2021 Mar 5. Biomark Med. 2021. PMID: 33666515
-
The biogenesis and biological functions of circular RNAs and their molecular diagnostic values in cancers.J Clin Lab Anal. 2020 Jan;34(1):e23049. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23049. Epub 2019 Sep 25. J Clin Lab Anal. 2020. PMID: 31556152 Free PMC article.
-
CircRNA, lncRNA, and mRNA profiles of umbilical cord blood exosomes from preterm newborns showing bronchopulmonary dysplasia.Eur J Pediatr. 2022 Sep;181(9):3345-3365. doi: 10.1007/s00431-022-04544-2. Epub 2022 Jul 5. Eur J Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 35790551 Free PMC article.
-
Functions of circular RNAs and their potential applications in gastric cancer.Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Feb;14(2):85-92. doi: 10.1080/17474124.2020.1715211. Epub 2020 Jan 14. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 31922886 Review.
Cited by
-
Translation role of circRNAs in cancers.J Clin Lab Anal. 2021 Jul;35(7):e23866. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23866. Epub 2021 Jun 7. J Clin Lab Anal. 2021. PMID: 34097315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CircRHOT1 restricts gastric cancer cell ferroptosis by epigenetically regulating GPX4.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2023 Aug 31;14(4):1715-1725. doi: 10.21037/jgo-23-550. Epub 2023 Aug 30. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37720433 Free PMC article.
-
Hsa_circ_0014784-induced YAP1 promoted the progression of pancreatic cancer by sponging miR-214-3p.Cell Cycle. 2023 Jul;22(13):1583-1596. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2023.2222519. Epub 2023 Jun 15. Cell Cycle. 2023. PMID: 37318258 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor suppressor role of hsa_circ_0035445 in gastric cancer.J Clin Lab Anal. 2021 Jun;35(6):e23727. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23727. Epub 2021 Apr 8. J Clin Lab Anal. 2021. PMID: 33830559 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA SET domain protein 3 promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma proliferation, cisplatin resistance, and protein kinase B / mammalian target of rapamycin pathway activation by modulating microRNA-147a expression.Bioengineered. 2022 Mar;13(3):5843-5854. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2036907. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35196205 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 91772279/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 201811646025/National Undergraduate Training Program for Innovation and Entrepreneurship
- 2017SRIP1918/Student Research and Innovation Program of Ningbo University
- 2018SRIP2507/Student Research and Innovation Program of Ningbo University
- 2019SRIP1902/Student Research and Innovation Program of Ningbo University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

