Natural compounds as inhibitors of transthyretin amyloidosis and neuroprotective agents: analysis of structural data for future drug design
- PMID: 32419519
- PMCID: PMC7301710
- DOI: 10.1080/14756366.2020.1760262
Natural compounds as inhibitors of transthyretin amyloidosis and neuroprotective agents: analysis of structural data for future drug design
Abstract
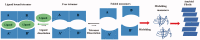
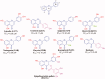
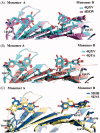
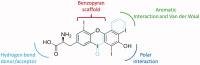
Natural compounds, such as plant and fruit extracts have shown neuroprotective effect against neurodegenerative diseases. It has been reported that several natural compounds binding to transthyretin (TTR) can be useful in amyloidosis prevention. TTR is a transporter protein that under physiological condition carries thyroxine (T4) and retinol in plasma and in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF); it also has a neuroprotective role against Alzheimer's disease (AD). However, TTR also is an amyloidogenic protein responsible for familial amyloid polyneuropathy (FAP) and familial amyloid cardiomyopathy (FAC). The TTR amyloidogenic potential is speeded up by several point mutations. One therapeutic strategy against TTR amyloidosis is the stabilisation of the native tetramer by natural compounds and small molecules. In this review, we examine the natural products that, starting from 2012 to present, have been studied as a stabiliser of TTR tetramer. In particular, we discussed the chemical and structural features which will be helpful for future drug design of new TTR stabilisers.
Keywords: Natural compounds; X-ray structure analysis; drug discovery; neuroprotection; transthyretin amyloid diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures


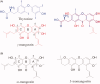
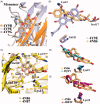
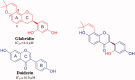
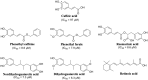



References
-
- Gordon MH. Dietary antioxidants in disease prevention. Nat Prod Rep 1996;13:265–73. - PubMed
-
- Ebrahimi A, Schluesener H.. Natural polyphenols against neurodegenerative disorders: potentials and pitfalls. Ageing Res Rev 2012;11:329–45. - PubMed
-
- Kamal M, Naz M, Jawaid T, Arif M.. Natural products and their active principles used in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases: a review. Orient Pharm Exp Med 2019;19:343–23.
-
- Pandey KB, Rizvi SI.. Current understanding of dietary polyphenols and their role in health and current understanding of dietary polyphenols and their role in health and disease. Curr Nutr Food Sci 2009;5: 249–263.
-
- Hung H, Joshipura KJ, Jiang R, et al. Fruit and vegetable intake and risk of major chronic disease. J Natl Cancer Inst 2004;96:1577–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
