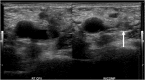
Deep venous thrombosis in a non-critically ill patient with novel COVID-19 infection
- PMID: 32419710
- PMCID: PMC7224655
- DOI: 10.1016/j.thromres.2020.05.015
Deep venous thrombosis in a non-critically ill patient with novel COVID-19 infection
Abstract
- •
COVID-19 infection is associated with hypercoagulability and a prothrombotic state.
- •
Little is understood about the prevalence of venous thromboembolism in mild disease.
- •
We present a case of mild COVID-19 complicated by extensive deep venous thrombosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest All authors contributed to the preparation of this manuscript. We have no conflicts of interest to disclose or any financial disclosures to report. The patient provided written consent for presentation of his case.
Figures
Similar articles
-
COVID-19 update: Covid-19-associated coagulopathy.J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2020 Jul;50(1):54-67. doi: 10.1007/s11239-020-02134-3. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2020. PMID: 32415579 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Thrombosis risk associated with COVID-19 infection. A scoping review.Thromb Res. 2020 Aug;192:152-160. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2020.05.039. Epub 2020 May 27. Thromb Res. 2020. PMID: 32485418 Free PMC article.
-
Ovarian vein thrombosis after coronavirus disease (COVID-19) infection in a pregnant woman: case report.J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2020 Oct;50(3):604-607. doi: 10.1007/s11239-020-02177-6. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2020. PMID: 32514763 Free PMC article.
-
Sofosbuvir for COVID-19 infection: A potential candidate.Indian J Pharmacol. 2020 May-Jun;52(3):232-233. doi: 10.4103/ijp.IJP_675_20. Epub 2020 Aug 4. Indian J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32874010 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Is the type of diabetes treatment relevant to outcome of COVID-19?J Diabetes. 2020 Jul;12(7):486-487. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.13047. J Diabetes. 2020. PMID: 32353193 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Randomized Study of Rivaroxaban vs Placebo on Disease Progression and Symptoms Resolution in High-Risk Adults With Mild Coronavirus Disease 2019.Clin Infect Dis. 2022 Aug 24;75(1):e473-e481. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciab813. Clin Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 34523673 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
COVID-19 in thrombosis research: An editorial perspective.Thromb Res. 2021 May;201:147-150. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2021.03.011. Epub 2021 Mar 24. Thromb Res. 2021. PMID: 33798826 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Thrombosis, an important piece in the COVID-19 puzzle: From pathophysiology to therapy.Anatol J Cardiol. 2021 Sep;25(9):601-608. doi: 10.5152/AnatolJCardiol.2021.475. Anatol J Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 34498590 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Late acute pulmonary embolism after mild Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): a case series.Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2020 Sep 4;62:e63. doi: 10.1590/S1678-9946202062063. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2020. PMID: 32901760 Free PMC article.
-
Thromboembolic disease in COVID-19 patients: A brief narrative review.J Intensive Care. 2020 Sep 14;8:70. doi: 10.1186/s40560-020-00483-y. eCollection 2020. J Intensive Care. 2020. PMID: 32939266 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhou F., Yu T., Du R., Fan G., Liu Y., Liu Z., Xiang J., Wang Y., Song B., Gu X., Guan L., Wei Y., Li H., Wu X., Xu J., Tu S., Zhang Y., Chen H., Cao B. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2020;395(10229):1054–1062. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lodigiani C., Iapichino G., Carenzo L., Cecconi M., Ferrazzi P., Sebastian T., Kucher N., Studt J.-D., Sacco C., Alexia B., Sandri M.T., Barco S. Venous and arterial thromboembolic complications in COVID-19 patients admitted to an academic hospital in Milan, Italy. Thromb. Res. 2020;191:9–14. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical