Endovascular Stroke Interventions: Procedural Complications and Management
- PMID: 32419733
- PMCID: PMC7224977
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0040-1709206
Endovascular Stroke Interventions: Procedural Complications and Management
Abstract
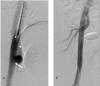
Endovascular mechanical thrombectomy has evolved significantly and has become the mainstay and most effective currently available treatment for acute ischemic stroke patients due to large vessel occlusion. Mechanical thrombectomy is presently performed using a stent retriever or stent-like device, an aspiration catheter, or a combination of the two. Much of the literature has focused on the benefits of endovascular mechanical thrombectomy with only limited data about procedural complications and management. Awareness of risk factors and early recognition of these complications can potentially reduce complication rates, improve management, and yield better overall outcomes. In this review, the authors present a description of intraprocedural complications and strategies to prevent and treat these complications.
Keywords: complication; hemorrhage; interventional radiology; stent; stroke.
© Thieme Medical Publishers.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest None declared.
Figures



References
-
- Balami J S, White P M, McMeekin P J, Ford G A, Buchan A M. Complications of endovascular treatment for acute ischemic stroke: Prevention and management. Int J Stroke. 2018;13(04):348–361. - PubMed
-
- Church E W, Gundersen A, Glantz M J, Simon S D. Number needed to treat for stroke thrombectomy based on a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2017;156:83–88. - PubMed
-
- Alawieh A, Vargas J, Fargen K M et al.Impact of procedure time on outcomes of thrombectomy for stroke. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;73(08):879–890. - PubMed
-
- Haussen D C, Nogueira R G, DeSousa K G et al.Transradial access in acute ischemic stroke intervention. J Neurointerv Surg. 2016;8(03):247–250. - PubMed

