Huzhang Tongfeng Granule Improves Monosodium Urate-Induced Inflammation of Gouty Arthritis Rat Model by Downregulation of Cyr61 and Related Cytokines
- PMID: 32419834
- PMCID: PMC7206887
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/9238797
Huzhang Tongfeng Granule Improves Monosodium Urate-Induced Inflammation of Gouty Arthritis Rat Model by Downregulation of Cyr61 and Related Cytokines
Abstract
Objective: Gouty arthritis (GA) is a noninfectious inflammatory disease characterized by self-limited and severe pain. Huzhang Tongfeng granule is one of the most effective traditional Chinese medicines in the treatment of acute GA. However, its effects on the inflammatory factors in the process of acute gout inflammation remain unknown. In the present study, we aimed to evaluate the effect of Huzhang Tongfeng granule on the expressions of Cyr61 and related inflammatory factors in both experimental gout models in vivo and in vitro.
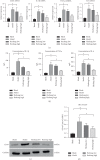
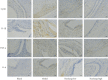
Methods: Huzhang Tongfeng granule was provided by the pharmaceutical preparation room of Yueyang Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine. The expressions of Cyr61, IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-6 in monosodium urate- (MSU-) induced rat models and fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs) were determined by RT-PCR, Western blotting analysis, ELISA, immunohistochemistry, and hematoxylin and eosin staining.
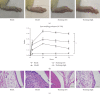
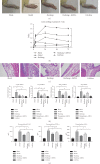
Results: Huzhang Tongfeng granule could downregulate the expressions of IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-6 to some extent by inhibiting the expression of Cyr61.
Conclusions: Collectively, our findings indicated that Cyr61 was highly expressed in rat models of gout. By inhibiting the expression of Cyr61, Huzhang Tongfeng granule could partially attenuate the inflammation induced by MSU crystal.
Copyright © 2020 Mi Zhou et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

